Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
GDExtension C++ example¶
Introducción¶
The C++ bindings for GDExtension are built on top of the C GDExtension API and provide a nicer way to "extend" nodes and other built-in classes in Godot using C++. This new system allows the extension of Godot to nearly the same level as statically linked C++ modules.
You can download the included example in the test folder of the godot-cpp repository on GitHub.
Configurando el proyecto¶
Hay algunos requisitos previos que necesitarás:
a Godot 4 executable,
un compilador de C++,
SCons como una herramienta de compilación,
una copia del repositorio godot-cpp.
También ve :ref:`Compilando<toc-devel-compiling>`ya que las herramientas de compilación son idénticas a las que necesitas para compilar Godot desde su código fuente.
You can download the godot-cpp repository from GitHub or let Git do the work for you. Note that this repository has different branches for different versions of Godot. GDExtensions will not work in older versions of Godot (only Godot 4 and up) and vice versa, so make sure you download the correct branch.
Nota
To use GDExtension
you need to use the godot-cpp branch that matches the version of Godot that you are
targeting. For example, if you're targeting Godot 4.1, use the 4.1 branch,
which is what is shown through out this tutorial.
The master branch is the development branch which is updated regularly
to work with Godot's master branch.
Advertencia
Our long-term goal is that GDExtensions targeting an earlier version of Godot will work in later minor versions, but not vice-versa. For example, a GDExtension targeting Godot 4.2 should work just fine in Godot 4.3, but one targeting Godot 4.3 won't work in Godot 4.2.
However, GDExtension is currently experimental, which means that we may break compatibility in order to fix major bugs or include critical features. For example, GDExtensions created for Godot 4.0 aren't compatible with Godot 4.1 (see Updating your GDExtension for 4.1).
If you are versioning your project using Git, it is recommended to add it as a Git submodule:
mkdir gdextension_cpp_example
cd gdextension_cpp_example
git init
git submodule add -b 4.1 https://github.com/godotengine/godot-cpp
cd godot-cpp
git submodule update --init
Alternatively, you can also clone it to the project folder:
mkdir gdextension_cpp_example
cd gdextension_cpp_example
git clone -b 4.1 https://github.com/godotengine/godot-cpp
Nota
If you decide to download the repository or clone it into your folder, make sure to keep the folder layout the same as we've setup here. Much of the code we'll be showcasing here assumes the project has this layout.
Si clonaste el ejemplo del enlace especificado en la introducción, los submódulos no son inicializados automáticamente. Tendrás que ejecutar los siguientes comandos:
cd gdextension_cpp_example
git submodule update --init
This will initialize the repository in your project folder.
Compilando las ligaduras de C++¶
Ya que descargamos los prerequisitos, es hora de compilar las ligaduras de C++.
El depósito contiene una copia de los metadatos de la versión actual de Godot, pero si quieres compilar las ligaduras para una versión más nueva de Godot, simplemente llama el ejecutable de Godot:
godot --dump-extension-api
The resulting extension_api.json file will be created in the executable's
directory. Copy it to the project folder and add custom_api_file=<PATH_TO_FILE>
to the scons command below.
To generate and compile the bindings, use this command (replacing <platform>
with windows, linux or macos depending on your OS):
The build process automatically detects the number of CPU threads to use for
parallel builds. To specify a number of CPU threads to use, add -jN at the
end of the SCons command line where N is the number of CPU threads to use.
cd godot-cpp
scons platform=<platform> custom_api_file=<PATH_TO_FILE>
cd ..
Este paso tomará tiempo en finalizar, una vez completo, deberías de tener unas bibliotecas estáticas que pueden ser compiladas dentro de tu proyecto guardado en godot-cpp/bin/.
Nota
Es posible que necesites agregar bits=64 al comando en Windows o Linux.
Creación de un simple plugin¶
Es hora de hacer un plugin real. Iniciaremos creando un proyecto de Godot vacío en el que colocaremos unos cuantos archivos.
Open Godot and create a new project. For this example, we will place it in a
folder called demo inside our GDExtension's folder structure.
En nuestro proyecto demo, crearemos una escena que contendrá un Nodo llamado "Main" y lo guardaremos como main.tscn. Volveremos a esto más tarde.
Back in the top-level GDExtension module folder, we're also going to create a
subfolder called src in which we'll place our source files.
You should now have demo, godot-cpp, and src
directories in your GDExtension module.
Your folder structure should now look like this:
gdextension_cpp_example/
|
+--demo/ # game example/demo to test the extension
|
+--godot-cpp/ # C++ bindings
|
+--src/ # source code of the extension we are building
In the src folder, we'll start with creating our header file for the
GDExtension node we'll be creating. We will name it gdexample.h:
#ifndef GDEXAMPLE_H
#define GDEXAMPLE_H
#include <godot_cpp/classes/sprite2d.hpp>
namespace godot {
class GDExample : public Sprite2D {
GDCLASS(GDExample, Sprite2D)
private:
double time_passed;
protected:
static void _bind_methods();
public:
GDExample();
~GDExample();
void _process(double delta) override;
};
}
#endif
There are a few things of note to the above. We include sprite2d.hpp which
contains bindings to the Sprite2D class. We'll be extending this class in our
module.
We're using the namespace godot, since everything in GDExtension is defined
within this namespace.
Then we have our class definition, which inherits from our Sprite2D through a
container class. We'll see a few side effects of this later on. The
GDCLASS macro sets up a few internal things for us.
Después de eso declaramos una sola variable de miembro llamada time_passed.
In the next block we're defining our methods, we have our constructor and destructor defined, but there are two other functions that will likely look familiar to some, and one new method.
The first is _bind_methods, which is a static function that Godot will
call to find out which methods can be called and which properties it exposes.
The second is our _process function, which will work exactly the same
as the _process function you're used to in GDScript.
Implementemos nuestras funciones creando nuestro archivo gdexample.cpp`:
#include "gdexample.h"
#include <godot_cpp/core/class_db.hpp>
using namespace godot;
void GDExample::_bind_methods() {
}
GDExample::GDExample() {
// Initialize any variables here.
time_passed = 0.0;
}
GDExample::~GDExample() {
// Add your cleanup here.
}
void GDExample::_process(double delta) {
time_passed += delta;
Vector2 new_position = Vector2(10.0 + (10.0 * sin(time_passed * 2.0)), 10.0 + (10.0 * cos(time_passed * 1.5)));
set_position(new_position);
}
This one should be straightforward. We're implementing each method of our class that we defined in our header file.
Note our _process function, which keeps track of how much time has passed
and calculates a new position for our sprite using a sine and cosine function.
There is one more C++ file we need; we'll name it register_types.cpp. Our
GDExtension plugin can contain multiple classes, each with their own header
and source file like we've implemented GDExample up above. What we need now
is a small bit of code that tells Godot about all the classes in our
GDExtension plugin.
#include "register_types.h"
#include "gdexample.h"
#include <gdextension_interface.h>
#include <godot_cpp/core/defs.hpp>
#include <godot_cpp/godot.hpp>
using namespace godot;
void initialize_example_module(ModuleInitializationLevel p_level) {
if (p_level != MODULE_INITIALIZATION_LEVEL_SCENE) {
return;
}
ClassDB::register_class<GDExample>();
}
void uninitialize_example_module(ModuleInitializationLevel p_level) {
if (p_level != MODULE_INITIALIZATION_LEVEL_SCENE) {
return;
}
}
extern "C" {
// Initialization.
GDExtensionBool GDE_EXPORT example_library_init(GDExtensionInterfaceGetProcAddress p_get_proc_address, const GDExtensionClassLibraryPtr p_library, GDExtensionInitialization *r_initialization) {
godot::GDExtensionBinding::InitObject init_obj(p_get_proc_address, p_library, r_initialization);
init_obj.register_initializer(initialize_example_module);
init_obj.register_terminator(uninitialize_example_module);
init_obj.set_minimum_library_initialization_level(MODULE_INITIALIZATION_LEVEL_SCENE);
return init_obj.init();
}
}
The initialize_example_module and uninitialize_example_module functions get
called respectively when Godot loads our plugin and when it unloads it. All
we're doing here is parse through the functions in our bindings module to
initialize them, but you might have to set up more things depending on your
needs. We call the function register_class for each of our classes in our library.
The important function is the third function called example_library_init.
We first call a function in our bindings library that creates an initialization object.
This object registers the initialization and termination functions of the GDExtension.
Furthermore, it sets the level of initialization (core, servers, scene, editor, level).
At last, we need the header file for the register_types.cpp named
register_types.h.
#ifndef GDEXAMPLE_REGISTER_TYPES_H
#define GDEXAMPLE_REGISTER_TYPES_H
#include <godot_cpp/core/class_db.hpp>
using namespace godot;
void initialize_example_module(ModuleInitializationLevel p_level);
void uninitialize_example_module(ModuleInitializationLevel p_level);
#endif // GDEXAMPLE_REGISTER_TYPES_H
Compilando el plugin¶
No podemos escribir fácilmente un archivo SConstruct a mano que SCons pueda usar para construir. Por propósito de este ejemplo, sólo :descarga: este archivo SConstruct <files/cpp_example/SConstruct> que hemos preparado. Cubriremos un ejemplo más personalizable y detallado de cómo usar estos archivos en próximos tutoriales.
Nota
This SConstruct file was written to be used with the latest godot-cpp
master, you may need to make small changes using it with older versions or
refer to the SConstruct file in the Godot 4.0 documentation.
Once you've downloaded the SConstruct file, place it in your GDExtension folder
structure alongside godot-cpp, src and demo, then run:
scons platform=<platform>
Ahora deberías poder encontrar el módulo en demo/bin/<platform>.
Nota
Here, we've compiled both godot-cpp and our gdexample library as debug
builds. For optimized builds, you should compile them using the
target=template_release switch.
Using the GDExtension module¶
Before we jump back into Godot, we need to create one more file in
demo/bin/.
This file lets Godot know what dynamic libraries should be
loaded for each platform and the entry function for the module. It is called gdexample.gdextension.
[configuration]
entry_symbol = "example_library_init"
compatibility_minimum = "4.1"
[libraries]
macos.debug = "res://bin/libgdexample.macos.template_debug.framework"
macos.release = "res://bin/libgdexample.macos.template_release.framework"
windows.debug.x86_32 = "res://bin/libgdexample.windows.template_debug.x86_32.dll"
windows.release.x86_32 = "res://bin/libgdexample.windows.template_release.x86_32.dll"
windows.debug.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.windows.template_debug.x86_64.dll"
windows.release.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.windows.template_release.x86_64.dll"
linux.debug.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_debug.x86_64.so"
linux.release.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_release.x86_64.so"
linux.debug.arm64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_debug.arm64.so"
linux.release.arm64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_release.arm64.so"
linux.debug.rv64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_debug.rv64.so"
linux.release.rv64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.linux.template_release.rv64.so"
android.debug.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.android.template_debug.x86_64.so"
android.release.x86_64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.android.template_release.x86_64.so"
android.debug.arm64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.android.template_debug.arm64.so"
android.release.arm64 = "res://bin/libgdexample.android.template_release.arm64.so"
This file contains a configuration section that controls the entry function of the module.
You should also set the minimum compatible Godot version with compatability_minimum,
which prevents older version of Godot from trying to load your extension.
The libraries section is the important bit: it tells Godot the location of the
dynamic library in the project's filesystem for each supported platform. It will
also result in just that file being exported when you export the project,
which means the data pack won't contain libraries that are incompatible with the
target platform.
Finally, the dependencies section allows you to name additional dynamic
libraries that should be included as well. This is important when your GDExtension
plugin implements someone else's library and requires you to supply a
third-party dynamic library with your project.
Here is another overview to check the correct file structure:
gdextension_cpp_example/
|
+--demo/ # game example/demo to test the extension
| |
| +--main.tscn
| |
| +--bin/
| |
| +--gdexample.gdextension
|
+--godot-cpp/ # C++ bindings
|
+--src/ # source code of the extension we are building
| |
| +--register_types.cpp
| +--register_types.h
| +--gdexample.cpp
| +--gdexample.h
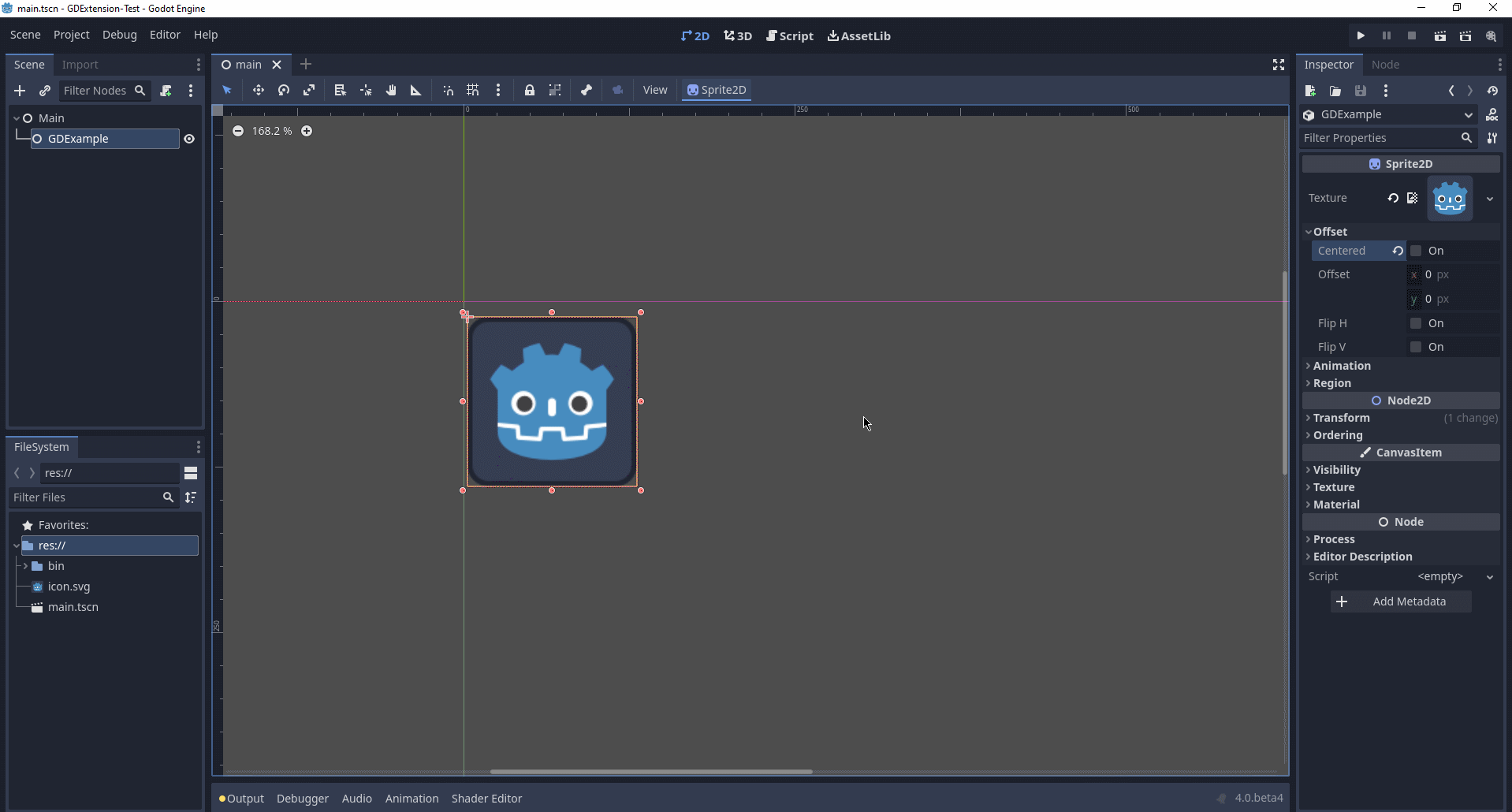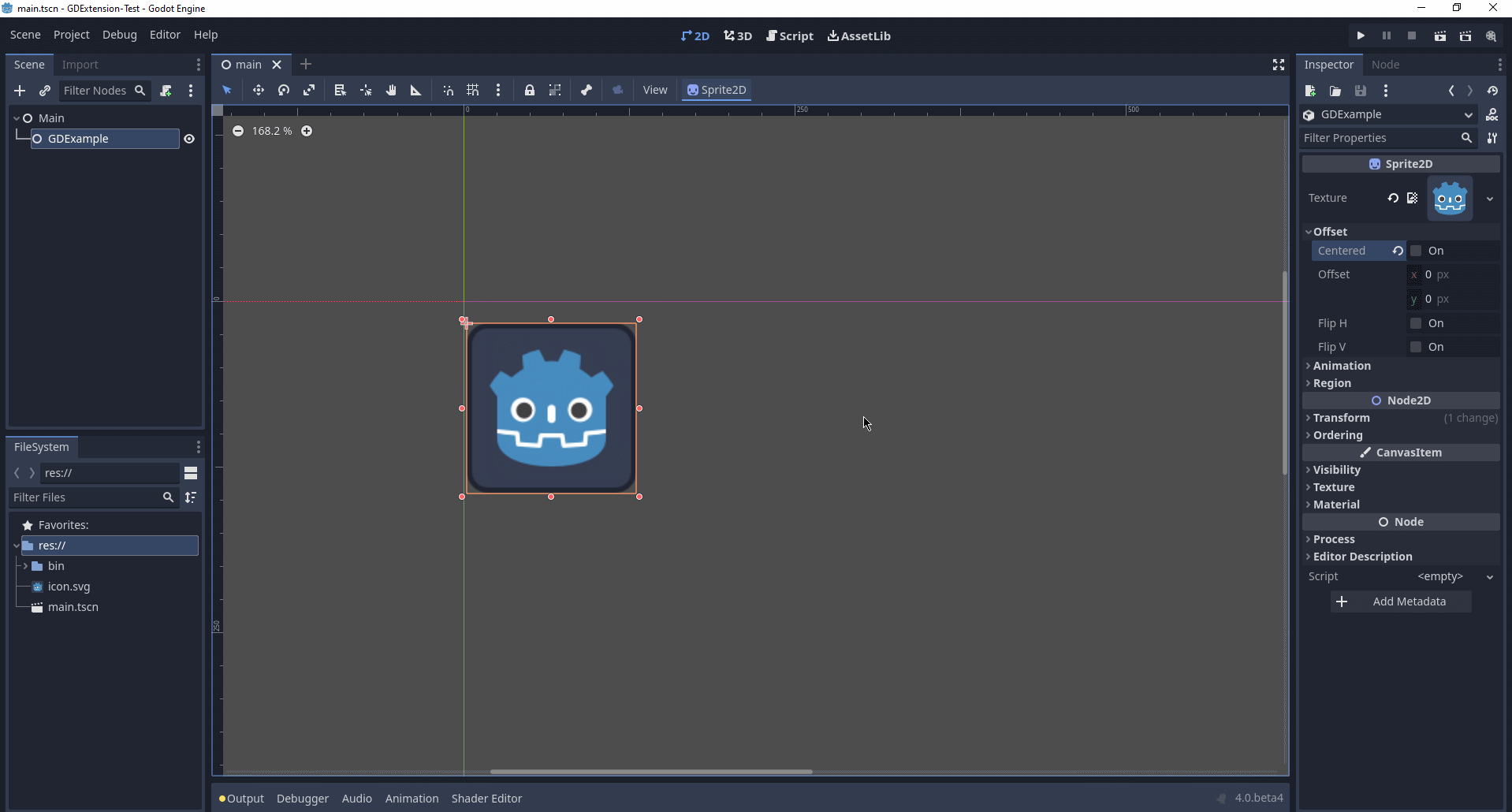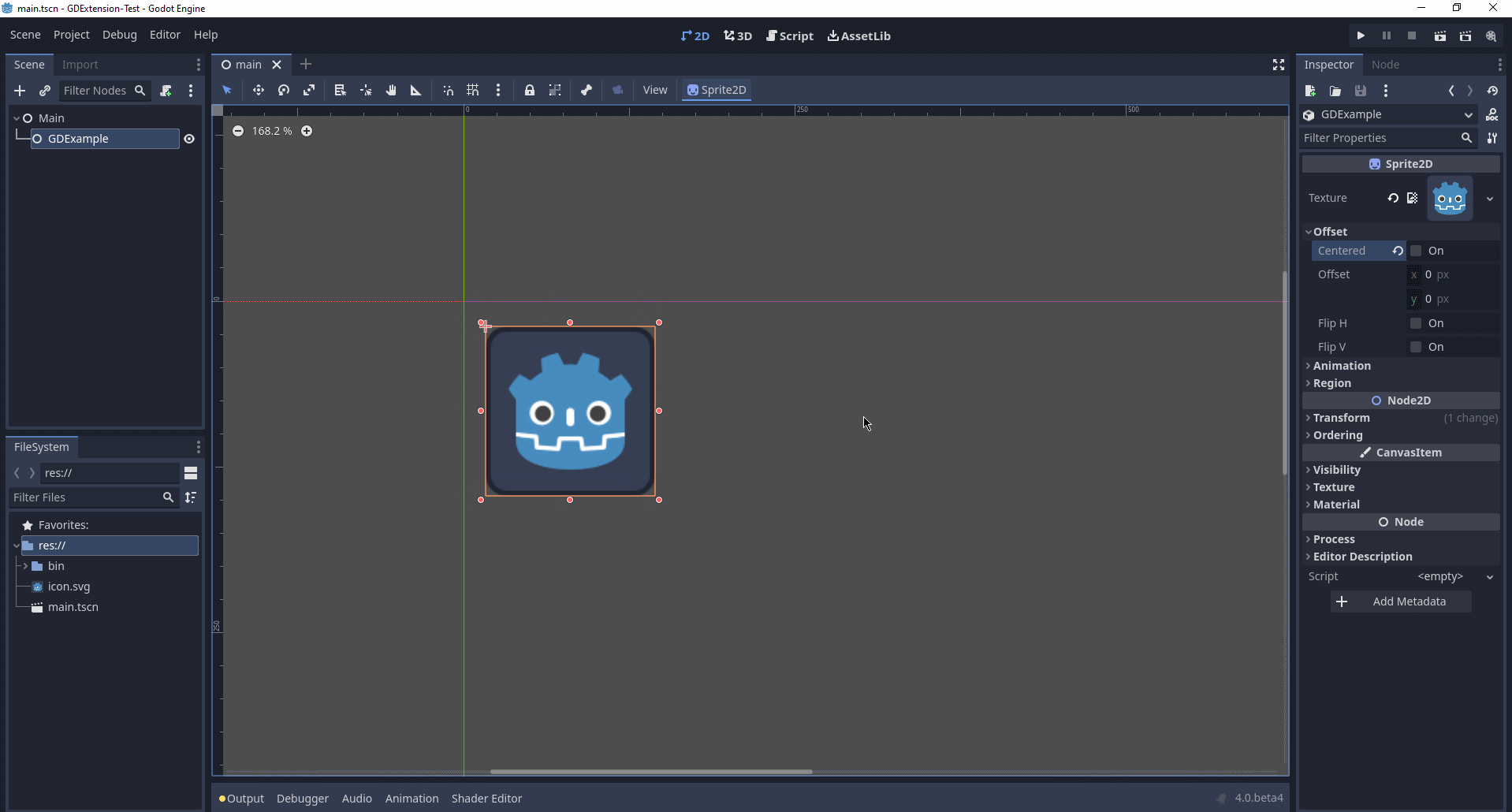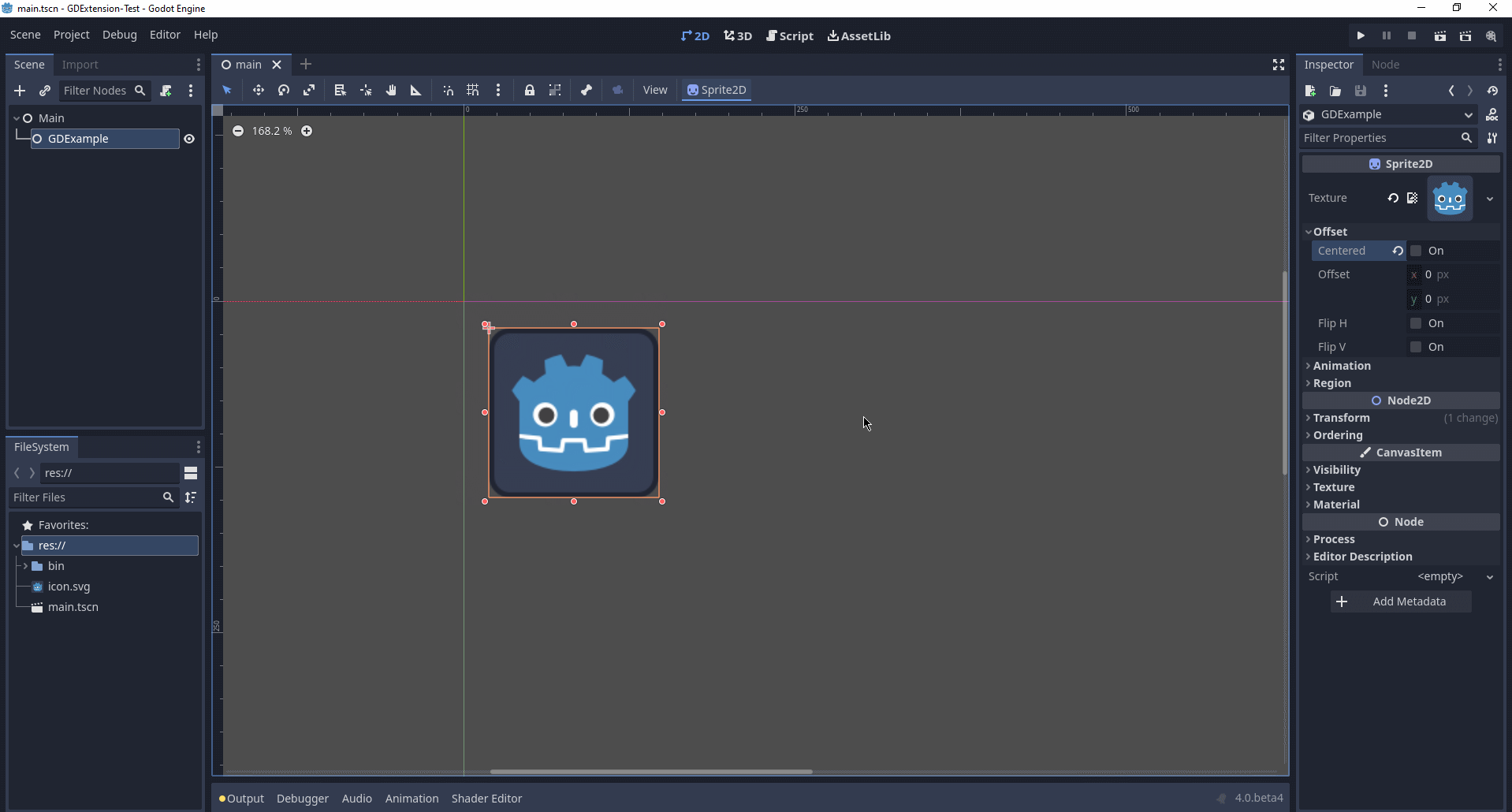
Time to jump back into Godot. We load up the main scene we created way back in the beginning and now add a newly available GDExample node to the scene:
We're going to assign the Godot logo to this node as our texture, disable the
centered property:
Finalmente, estamos listos para ejecutar el proyecto:
Custom editor icon¶
By default, Godot uses the node icon in the scene dock for GDExtension nodes. The custom icon can be
added via the gdextension file. The node's icon is set by reference to its name and resource path
of an SVG file.
Por ejemplo:
[icons]
GDExample = "res://icons/gd_example.svg"
The path should point to a 16 by 16 pixel SVG image. Read the guide for creating icons for more information.
Agregando propiedades¶
GDScript allows you to add properties to your script using the export
keyword. In GDExtension you have to register the properties with a getter and
setter function or directly implement the _get_property_list, _get and
_set methods of an object (but that goes far beyond the scope of this
tutorial).
Lets add a property that allows us to control the amplitude of our wave.
In our gdexample.h file we need to add a member variable and getter and setter
functions:
...
private:
double time_passed;
double amplitude;
public:
void set_amplitude(const double p_amplitude);
double get_amplitude() const;
...
En nuestro archivo gdexample.cpp, necesitaremos realizar una serie de cambios. Solo mostraremos los métodos que terminamos modificando, sin eliminar las líneas que estamos omitiendo:
void GDExample::_bind_methods() {
ClassDB::bind_method(D_METHOD("get_amplitude"), &GDExample::get_amplitude);
ClassDB::bind_method(D_METHOD("set_amplitude", "p_amplitude"), &GDExample::set_amplitude);
ClassDB::add_property("GDExample", PropertyInfo(Variant::FLOAT, "amplitude"), "set_amplitude", "get_amplitude");
}
GDExample::GDExample() {
// Initialize any variables here.
time_passed = 0.0;
amplitude = 10.0;
}
void GDExample::_process(double delta) {
time_passed += delta;
Vector2 new_position = Vector2(
amplitude + (amplitude * sin(time_passed * 2.0)),
amplitude + (amplitude * cos(time_passed * 1.5))
);
set_position(new_position);
}
void GDExample::set_amplitude(const double p_amplitude) {
amplitude = p_amplitude;
}
double GDExample::get_amplitude() const {
return amplitude;
}
Una vez que compiles el módulo con estos cambios implementados, verás que se ha agregado una propiedad a nuestra interfaz. Ahora puedes cambiar esta propiedad y, cuando ejecutes tu proyecto, notarás que el ícono de Godot se desplaza a lo largo de una figura más grande.
Hagamos lo mismo, pero para la velocidad de nuestra animación y usemos una función setter y getter. Nuestro archivo de encabezado gdexample.h solo necesita unas pocas líneas más de código:
...
double amplitude;
double speed;
...
void _process(double delta) override;
void set_speed(const double p_speed);
double get_speed() const;
...
Esto requiere algunos cambios adicionales en nuestro archivo gdexample.cpp. Nuevamente, solo mostraremos los métodos que han cambiado, así que no eliminaré nada de lo que estamos omitiendo:
void GDExample::_bind_methods() {
...
ClassDB::bind_method(D_METHOD("get_speed"), &GDExample::get_speed);
ClassDB::bind_method(D_METHOD("set_speed", "p_speed"), &GDExample::set_speed);
ClassDB::add_property("GDExample", PropertyInfo(Variant::FLOAT, "speed", PROPERTY_HINT_RANGE, "0,20,0.01"), "set_speed", "get_speed");
}
GDExample::GDExample() {
time_passed = 0.0;
amplitude = 10.0;
speed = 1.0;
}
void GDExample::_process(double delta) {
time_passed += speed * delta;
Vector2 new_position = Vector2(
amplitude + (amplitude * sin(time_passed * 2.0)),
amplitude + (amplitude * cos(time_passed * 1.5))
);
set_position(new_position);
}
...
void GDExample::set_speed(const double p_speed) {
speed = p_speed;
}
double GDExample::get_speed() const {
return speed;
}
Now when the project is compiled, we'll see another property called speed. Changing its value will make the animation go faster or slower. Furthermore, we added a property range which describes in which range the value can be. The first two arguments are the minimum and maximum value and the third is the step size.
Nota
For simplicity, we've only used the hint_range of the property method. There are a lot more options to choose from. These can be used to further configure how properties are displayed and set on the Godot side.
Señales¶
Last but not least, signals fully work in GDExtension as well. Having your extension
react to a signal given out by another object requires you to call connect
on that object. We can't think of a good example for our wobbling Godot icon, we
would need to showcase a far more complete example.
Esta es la sintaxis requerida:
some_other_node->connect("the_signal", Callable(this, "my_method"));
To connect our signal the_signal from some other node with our method
my_method, we need to provide the connect method with the name of the signal
and a Callable. The Callable holds information about an object on which a method
can be called. In our case, it associates our current object instance this with the
method my_method of the object. Then the connect method will add this to the
observers of the_signal. Whenever the_signal is now emitted, Godot knows which
method of which object it needs to call.
Note that you can only call my_method if you've previously registered it in
your _bind_methods method. Otherwise Godot will not know about the existence
of my_method.
To learn more about Callable, check out the class reference here: Callable.
Enviar señales desde tu objeto es más común. Para nuestro icono de Godot tembloroso, haremos algo simple solo para mostrar cómo funciona. Emitiremos una señal cada vez que pase un segundo y pasaremos la nueva ubicación a lo largo de ella.
En nuestro archivo de encabezado gdexample.h, necesitamos definir un nuevo miembro llamado time_emit:
...
double time_passed;
double time_emit;
double amplitude;
...
Esta vez, los cambios en gdexample.cpp son más elaborados. Primero, necesitarás establecer time_emit = 0.0; ya sea en nuestro método _init o en nuestro constructor. Veremos los otros 2 cambios necesarios uno por uno.
In our _bind_methods method, we need to declare our signal. This is done
as follows:
void GDExample::_bind_methods() {
...
ClassDB::add_property("GDExample", PropertyInfo(Variant::FLOAT, "speed", PROPERTY_HINT_RANGE, "0,20,0.01"), "set_speed", "get_speed");
ADD_SIGNAL(MethodInfo("position_changed", PropertyInfo(Variant::OBJECT, "node"), PropertyInfo(Variant::VECTOR2, "new_pos")));
}
Here, our ADD_SIGNAL macro can be a single call with a MethodInfo argument.
MethodInfo's first parameter will be the signal's name, and its remaining parameters
are PropertyInfo types which describe the essentials of each of the method's parameters.
PropertyInfo parameters are defined with the data type of the parameter, and then the name
that the parameter will have by default.
So here, we add a signal, with a MethodInfo which names the signal "position_changed". The
PropertyInfo parameters describe two essential arguments, one of type Object, the other
of type Vector2, respectively named "node" and "new_pos".
A continuación, necesitaremos cambiar nuestro método _process:
void GDExample::_process(double delta) {
time_passed += speed * delta;
Vector2 new_position = Vector2(
amplitude + (amplitude * sin(time_passed * 2.0)),
amplitude + (amplitude * cos(time_passed * 1.5))
);
set_position(new_position);
time_emit += delta;
if (time_emit > 1.0) {
emit_signal("position_changed", this, new_position);
time_emit = 0.0;
}
}
Después de haber pasado un segundo, emitimos nuestra señal y reiniciamos nuestro contador. Podemos agregar los valores de los parámetros directamente a emit_signal.
Once the GDExtension library is compiled, we can go into Godot and select our sprite node. In the Node dock, we can find our new signal and link it up by pressing the Connect button or double-clicking the signal. We've added a script on our main node and implemented our signal like this:
extends Node
func _on_Sprite2D_position_changed(node, new_pos):
print("The position of " + node.get_class() + " is now " + str(new_pos))
Cada segundo, mostramos nuestra posición en la consola.
Siguientes pasos¶
We hope the above example showed you the basics. You can build upon this example to create full-fledged scripts to control nodes in Godot using C++.