Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Primeiras impressões do editor do Godot¶
Esta página lhe dará uma breve visão geral da interface do Godot. Vamos ver as diferentes telas principais e painéis para ajudá-lo a se situar.
Ver também
Para uma descrição mais detalhada da interface do editor e como utilizá-la, veja o Manual do editor.
The Project Manager¶
When you launch Godot, the first window you see is the Project Manager. In the default tab Local Projects, you can manage existing projects, import or create new ones, and more.
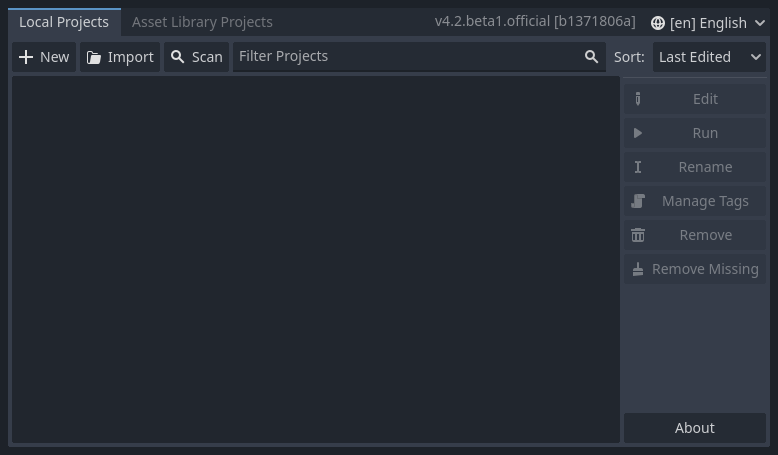
At the top of the window, there is another tab named "Asset Library Projects". You can search for demo projects in the open source asset library, which includes many projects developed by the community.
Ver também
To learn the Project Manager's ins and outs, read Using the Project Manager.
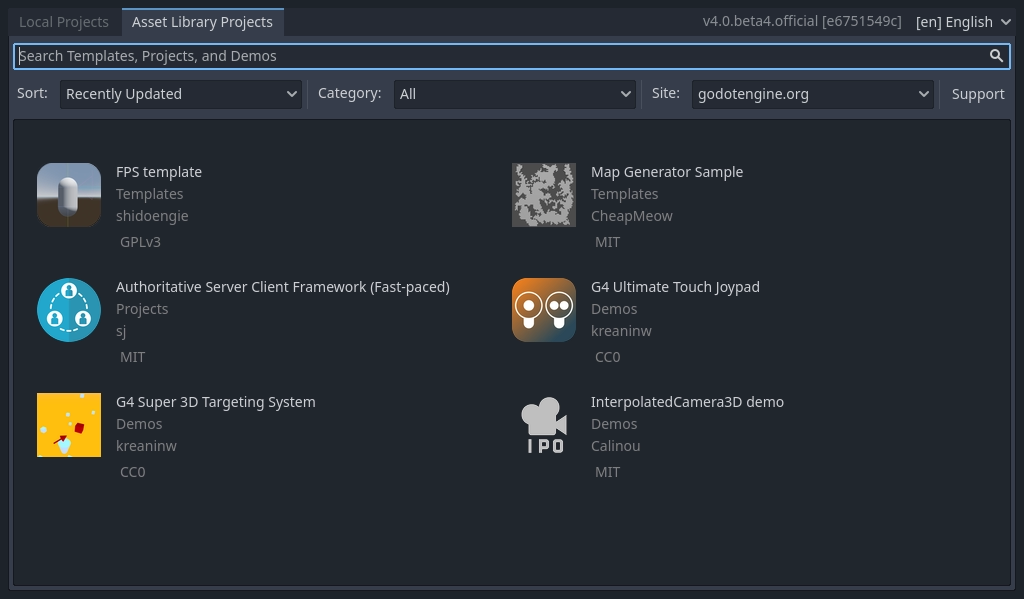
Você pode também mudar o idioma do editor utilizando o menu suspenso à direita da versão do motor(engine), no canto superior direito da janela. Por padrão, está em English (EN).

Primeiras impressões do editor do Godot¶
Quando você abre um projeto novo ou existente, a interface do editor aparece. Vejamos suas principais áreas.
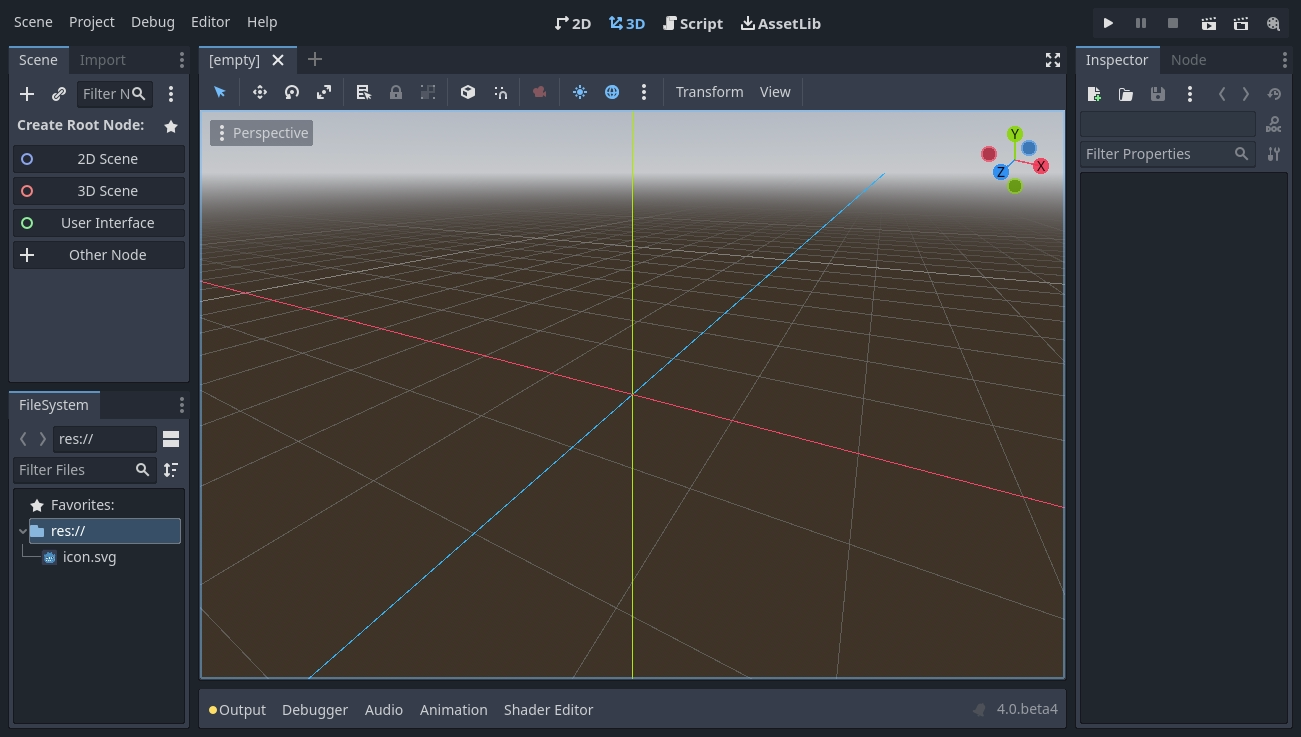
Por padrão, aparece menus, telas principais, e os botões de teste no canto superior da janela.

No centro está a janela de visualização (viewport) com sua barra de ferramenta (toolbar) no topo, onde você encontra as ferramentas para mover, redimensionar ou travar nós da sua cena.
Em ambos os lados da janela de exibição estão os painéis. E na parte inferior da janela encontra-se o painel inferior.
A barra de ferramentas muda baseado no contexto e no nó selecionado. Aqui está a barra de ferramentas 2D.

Abaixo sua versão 3D.

Let's look at the docks. The FileSystem dock lists your project files, including scripts, images, audio samples, and more.
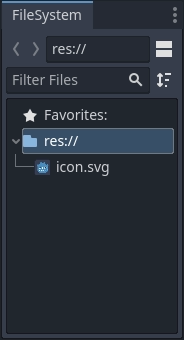
O painel Cena lista os nós da cena ativa.
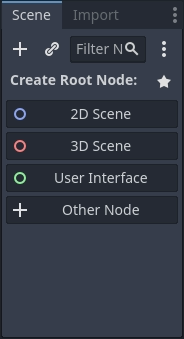
O Inspetor te permite editar as propriedades de um nó selecionado.
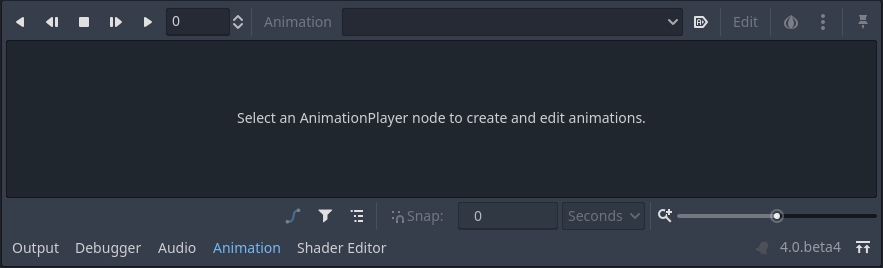
O Painel Inferior, abaixo da janela principal(viewport), é onde fica o console de depuração, o editor de animação e o mixer de áudio. Eles são largos e podem ocupar bastante espaço, por isso eles ficam minimizados por padrão.

Quando você clica em um deles, ele expande verticalmente. Abaixo você pode ver o editor de animações aberto.
As quatro cenas principais¶
Há quatro botões na tela principal, centralizados no topo do editor: 2D, 3D, Script e AssetLib.
Você usará a tela 2D para todos os tipos de jogos. Além dos jogos 2D, a tela 2D é onde você construirá suas interfaces.
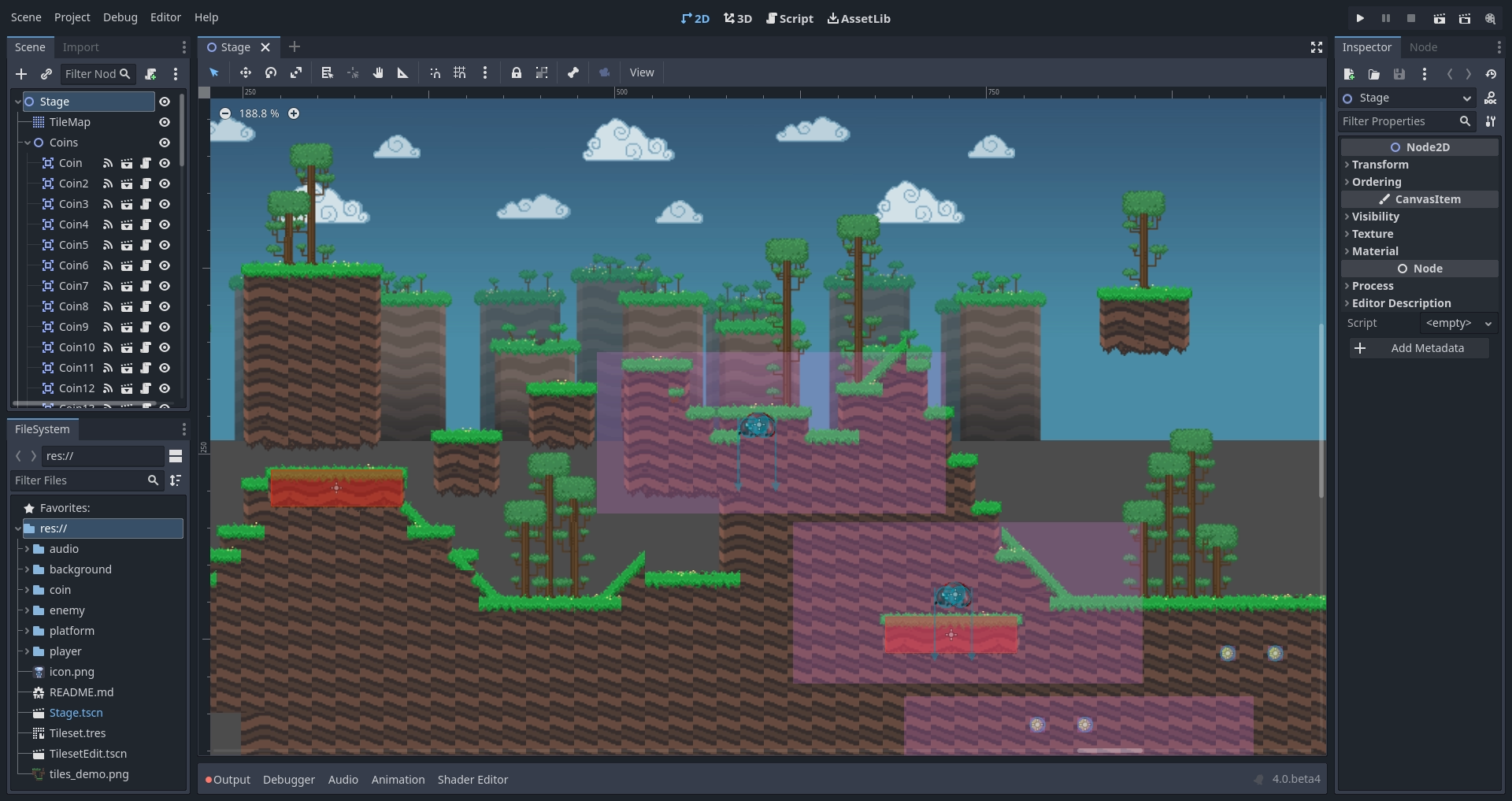
Na tela 3D, você pode trabalhar com malhas (meshes), luzes e a criação de leveis para jogos 3D.
Observe o botão Perspectiva sob a barra de ferramentas. Clicar nele abre uma lista de opções relacionadas à visualização 3D.
Nota
Leia Introdução ao 3D para saber mais sobre a tela principal 3D.
A tela Script é um editor de código completo com um depurador, preenchimento automático avançado e referência de código integrada.
Finally, the AssetLib is a library of free and open source add-ons, scripts, and assets to use in your projects.
Ver também
Você pode aprender mais sobre a biblioteca de assets em Sobre a Biblioteca de Assets.
Documentação integrada¶
Godot vem com a documentão de referência de classe integrada.
Você pode procurar informações sobre uma classe, método, propriedade, ou sinal usando qualquer um dos métodos seguintes:
Pressing F1 (or Alt + Space on macOS, or fn + F1 for laptops with a fn key) anywhere in the editor.
Clicando no botão "Pesquisar Ajuda" no canto superior direito da tela principal do Script.
Clicando no menu de Ajuda e Pequisar Ajuda.
Clicar enquanto pressiona a tecla Ctrl em um nome de classe, nome de função ou variável incorporada no editor de script.

Quando você faz qualquer um desses, uma janela aparece. Digite para pesquisar qualquer item. Você também pode usá-lo para procurar objetos e métodos disponíveis.
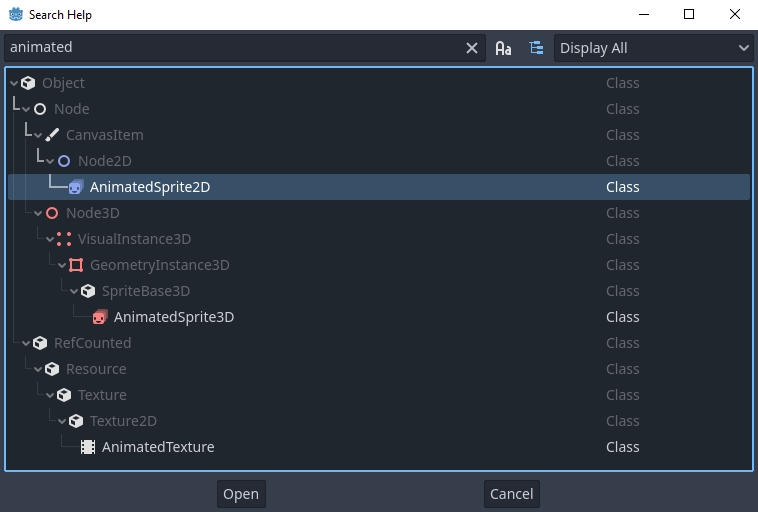
Clique duas vezes em um item para abrir a página correspondente na tela principal do script.