Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Solução de problemas¶
Esta página lista problemas comuns ao usar o Godot e possíveis soluções.
Ver também
See Utilizando o editor Web for caveats specific to the Web version of the Godot editor.
O editor roda lento e usa todos os recursos do meu CPU e da GPU, fazendo meu computador barulhento¶
This is a known issue, especially on macOS since most Macs have Retina displays. Due to Retina displays' higher pixel density, everything has to be rendered at a higher resolution. This increases the load on the GPU and decreases perceived performance.
There are several ways to improve performance and battery life:
Em 3D, clique no botão Perspectiva no canto superior esquerdo e habilite Metade da Resolução. Agora o jogo será renderizado na 3D viewport com metade da resolução, deixando em até 4x mais rapido.
Abra as Configurações do Editor e aumento o valor de Modo de baixo processamento tempo (µsec) para
33000(30 PFS). Essa valor determina a quantidade de microssegundos entre os frames a serem renderizados. Valores altos farão o editor pareça ser menos reativo, mas ajudará reduzindo significativamente o uso da CPU e GPU.Se você tem outro nó que faça o editor redesenhe continuamente (partículas, por exemplo), oculte-o e o mostre pelo script usando o método
_ready. Desta maneira ele estará oculto no editor, mas visível no projeto em execução.
O editor tem stutters e flickes no meu monitor com refresh rate variável (G-Sync/FreeSync)¶
This is a known issue. Variable refresh rate monitors need to adjust their gamma curves continuously to emit a consistent amount of light over time. This can cause flicker to appear in dark areas of the image when the refresh rate varies a lot, which occurs as the Godot editor only redraws when necessary.
There are several workarounds for this:
Enable Interface > Editor > Update Continuously in the Editor Settings. Keep in mind this will increase power usage and heat/noise emissions since the editor will now be rendering constantly, even if nothing has changed on screen. To alleviate this, you can increase Low Processor Mode Sleep (µsec) to
33000(30 FPS) in the Editor Settings. This value determines the amount of microseconds between frames to render. Higher values will make the editor feel less reactive but will help decrease CPU and GPU usage significantly.Alternatively, disable variable refresh rate on your monitor or in the graphics driver.
VRR flicker can be reduced on some displays using the VRR Control or Fine Tune Dark Areas options in your monitor's OSD. These options may increase input lag or result in crushed blacks.
Se você esta usando uma tela OLED, use o tema do editor **Black (OLED) presente nas configurações do editor. Isto oculta os Flickers do VRR graças aos níveis perfeitos de preto do OLED.
O editor ou projeto leva muito tempo para iniciar¶
Quando você usar um dos renderizadores de base Vulkan (Avançado+ ou Mobile), a primeira inicialização é esperado que seja relativamente longa. Isto ocorre porque os shaders precisam ser compilados antes de serem armazenados em cache. Os shaders também precisam ser armazenados em cache novamente após uma atualização da Godot, depois de atualizar os drivers de vídeo ou após trocar de placa de vídeo.
Esse é um bug conhecido no Windows quando você tem periféricos USB específicos conectados. Em particular, o software iCUE da Corsair parece causar o bug. Tente atualizar os drivers dos seus periféricos USB para a última versão. Se o bug persistir, você precisa desconectar os periféricos com defeito antes de abrir o editor. Após isso, você pode conectá-lo novamente.
Firewall software such as Portmaster may also cause the debug port to be
blocked. This causes the project to take a long time to start, while being
unable to use debugging features in the editor (such as viewing print()
output). You can work this around by changing the debug port used by the project
in the Editor Settings (Network > Debug > Remote Port). The default is
6007; try another value that is greater than 1024, such as 7007.
O editor do Godot parece congelar após clicar no console do sistema¶
Ao executar o Godot no Windows com o console do sistema aberto, você pode acidentalmente habilitar o modo de seleção clicando dentro da janela de comando. Esse comportamento específico do Windows pausa o aplicativo para que você selecione o texto dentro do console do sistema. O Godot não pode ignorar esse comportamento específico do sistema.
Para resolver isto, selecione a janela do console do sistema e pressione Enter para sair do modo de seleção.
O icon do painel do editor da Godot no mac'os é duplicado toda vez que é movido manualmente¶
Se você abrir o editor da Godot e mudar a posição manualmente do ícone do painel, quando você reiniciar o editor, você terá um ícone do painel duplicado á direita do painel.
Isto ocorre devido a limitação de designer do painel do macOS. A unica maneira conhecida de resolver isto é alterando colocando o gerenciador de projetos em uma único processo, fazendo que o o gerenciador de projetos não abrisse um processo separado quando inicia-se o editor. Embora o uso de um única instancia processo possa trazer vários benefícios, não há um planejamento para realizar essa tarefa devido a sua complexidade.
To avoid this issue, keep the Godot editor's dock icon at its default location as created by macOS.
Some text such as "NO DC" appears in the top-left corner of the Project Manager and editor window¶
Isso é devido ao driver gráfico da NVIDIA injetando um overlay para mostrar informações.
Para desabilitar esse overlay no Windows, restaure suas configurações do driver gráfico para os valores padrões no Painel de Controle NVIDIA.
Para desabilitar esse overlay no Linux, abra nvidia-settings, vá até X Screen 0 > OpenGL Settings e desmarque Enable Graphics API Visual Indicator.
The editor or project appears overly sharp or blurry¶
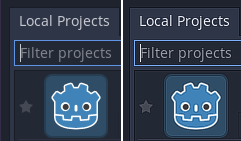
Correct appearance (left), oversharpened appearance due to graphics driver sharpening (right)¶
If the editor or project appears overly sharp, this is likely due to image sharpening being forced on all Vulkan or OpenGL applications by your graphics driver. You can disable this behavior in the graphics driver's control panel:
NVIDIA (Windows): Open the start menu and choose NVIDIA Control Panel. Open the Manage 3D settings tab on the left. In the list in the middle, scroll to Image Sharpening and set it to Sharpening Off.
AMD (Windows): Open the start menu and choose AMD Software. Click the settings "cog" icon in the top-right corner. Go to the Graphics tab then disable Radeon Image Sharpening.
If the editor or project appears overly blurry, this is likely due to FXAA being forced on all Vulkan or OpenGL applications by your graphics driver.
NVIDIA (Windows): Open the start menu and choose NVIDIA Control Panel. Open the Manage 3D settings tab on the left. In the list in the middle, scroll to Fast Approximate Antialiasing and set it to Application Controlled.
NVIDIA (Linux): Open the applications menu and choose NVIDIA X Server Settings. Select to Antialiasing Settings on the left, then uncheck Enable FXAA.
AMD (Windows): Open the start menu and choose AMD Software. Click the settings "cog" icon in the top-right corner. Go to the Graphics tab, scroll to the bottom and click Advanced to unfold its settings. Disable Morphological Anti-Aliasing.
Third-party vendor-independent utilities such as vkBasalt may also force sharpening or FXAA on all Vulkan applications. You may want to check their configuration as well.
After changing options in the graphics driver or third-party utilities, restart Godot to make the changes effective.
If you still wish to force sharpening or FXAA on other applications, it's recommended to do so on a per-application basis using the application profiles system provided by graphics drivers' control panels.
The editor or project appears to have washed out colors¶
On Windows, this is usually caused by incorrect OS or monitor settings, as Godot currently does not support HDR output (even though it may internally render in HDR).
As most displays are not designed to display SDR content in HDR mode, it is recommended to disable HDR in the Windows settings when not running applications that use HDR output. On Windows 11, this can be done by pressing Windows + Alt + B (this shortcut is part of the Xbox Game Bar app). To toggle HDR automatically based on applications currently running, you can use AutoActions.
If you insist on leaving HDR enabled, it is possible to somewhat improve the result by ensuring the display is configured to use HGIG tonemapping (as opposed to DTM), then using the Windows HDR calibration app. It is also strongly recommended to use Windows 11 instead of Windows 10 when using HDR. The end result will still likely be inferior to disabling HDR on the display, though.
Support for HDR output is planned in a future release.
The editor/project freezes or displays glitched visuals after resuming the PC from suspend¶
This is a known issue on Linux with NVIDIA graphics when using the proprietary driver. There is no definitive fix yet, as suspend on Linux + NVIDIA is often buggy when OpenGL or Vulkan is involved. The Compatibility rendering method (which uses OpenGL) is generally less prone to suspend-related issues compared to the Forward+ and Forward Mobile rendering methods (which use Vulkan).
The NVIDIA driver offers an experimental option to preserve video memory after suspend which may resolve this issue. This option has been reported to work better with more recent NVIDIA driver versions.
To avoid losing work, save scenes in the editor before putting the PC to sleep.
The project works when run from the editor, but fails to load some files when running from an exported copy¶
Isso é geralmente causado ao esquecer de especificar um filtro para arquivos sem recursos no diálogo Exportar. Por padrão, Godot somente incluirá recursos presentes no arquivo PCK. Alguns arquivos comumente usados, como arquivos JSON, não são considerados recursos. Por exemplo, se você carregar test.json no projeto exportado, você precisa especificar *.json no filtro de exportação sem recursos. Veja Opções de recursos para mais informação.
Also, note that files and folders whose names begin with a period will never be
included in the exported project. This is done to prevent version control
folders like .git from being included in the exported PCK file.
No Windows, isso também pode ser devido a problemas de sensibilidade de maiúsculas e minúsculas. Se você fizer referência a um recurso em seu script com maiúsculas e minúsculas diferentes das do sistema de arquivos, o carregamento falhará quando você exportar o projeto. Isso ocorre porque o sistema de arquivos PCK virtual diferencia maiúsculas de minúsculas, enquanto o sistema de arquivos do Windows não diferencia maiúsculas de minúsculas por padrão.