Android-Plugins erstellen¶
Einführung¶
Android plugins are powerful tools to extend the capabilities of the Godot engine by tapping into the functionality provided by the Android platform and ecosystem.
Die Umwandlung von Werten in Geld bei mobilen Spielen ist ein Beispiel dafür, dass Funktionen und Fähigkeiten erforderlich sind, die nicht zu den Kernfunktionen einer Spiele-Engine gehören:
Analytiken
In-App Käufe
Beleg-Überprüfung
Installation von Tracking
Werbung
Werbevideos
Übergreifende Werbung (Cross-Promotion)
Weiche und harte Währungen im Spiel
Promo-Codes
A/B Tests
Login
speichern in der Cloud
Bestenlisten und Punktzahlen
Benutzerunterstützung & Feedback
Posting auf Facebook, Twitter usw.
Mitteilungen
Android Plugins¶
While introduced in Godot 3.2, the Android plugin system got a significant architecture update starting with Godot 3.2.2.
The new plugin system is backward-incompatible with the previous one, but both systems are kept functional in future releases of the 3.2.x branch.
Since we previously did not version the Android plugin systems, the new one is now labelled v1 and is the starting point for the modern Godot Android ecosystem.
Hinweis: In Godot 4.0 wird das vorherige System vollständig veraltet sein und entfernt werden.
As a prerequisite, make sure you understand how to set up a custom build environment for Android.
At its core, a Godot Android plugin is a Android archive library (aar archive file) with the following caveats:
The library must have a dependency on the Godot engine library (
godot-lib.<version>.<status>.aar). A stable version is made available for each Godot release on the Godot download page.Die Bibliothek muss ein speziell konfiguriertes
<meta-data>-Tag in ihrer Manifestdatei enthalten.
Erstellen von Android Plugins¶
Prerequisite: Android Studio is strongly recommended as the IDE to use to create Android plugins. The instructions below assumes that you're using Android Studio.
Folgen Sie diesen Anweisungen, um ein Android-Bibliotheksmodul für Ihr Plugin zu erstellen.
Fügen Sie die Godot-Engine-Bibliothek als Abhängigkeit zu Ihrem Plugin-Modul hinzu:
Download the Godot engine library (
godot-lib.<version>.<status>.aar) from the Godot download page (e.g.:godot-lib.3.4.2.stable.release.aar).Follow these instructions to add the Godot engine library as a dependency for your plugin.
In the plugin module's
build.gradlefile, replaceimplementationwithcompileOnlyfor the dependency line for the Godot engine library.
Create a new class in the plugin module and make sure it extends
org.godotengine.godot.plugin.GodotPlugin. At runtime, it will be used to instantiate a singleton object that will be used by the Godot engine to load, initialize and run the plugin.Aktualisieren Sie die Plugin-Datei
AndroidManifest.xml:
Öffnen Sie die Plugin-Datei
AndroidManifest.xml.Fügen Sie den
<application></application>-Tag hinzu, falls er fehlt.Fügen Sie im
<application>Tag ein<meta-data>Tag-Setup wie folgt hinzu:<meta-data android:name="org.godotengine.plugin.v1.[PluginName]" android:value="[plugin.init.ClassFullName]" />Where
PluginNameis the name of the plugin, andplugin.init.ClassFullNameis the full name (package + class name) of the plugin loading class.
Add the remaining logic for your plugin and run the
gradlew buildcommand to generate the plugin'saarfile. The build will likely generate both adebugandreleaseaarfiles. Depending on your need, pick only one version (usually thereleaseone) which to provide your users with.It's recommended that the
aarfilename matches the following pattern:[PluginName]*.aarwherePluginNameis the name of the plugin in PascalCase (e.g.:GodotPayment.release.aar).Create a Godot Android Plugin configuration file to help the system detect and load your plugin:
Die Erweiterung der Konfigurationsdatei muss
gdapsein (z.B.:MyPlugin.gdap).Das Konfigurationsdateiformat lautet wie folgt:
[config] name="MyPlugin" binary_type="local" binary="MyPlugin.aar" [dependencies] local=["local_dep1.aar", "local_dep2.aar"] remote=["example.plugin.android:remote-dep1:0.0.1", "example.plugin.android:remote-dep2:0.0.1"] custom_maven_repos=["http://repo.mycompany.com/maven2"]Der Abschnitt
configund dessen Felder sind erforderlich und wie folgt definiert:
name: Name des Plugins.
binary_type: kann entweder
localoderremotesein. Der Typ beeinflusst das Feld binary.binary:
If binary_type is
local, then this should be the filepath of the pluginaarfile.
The filepath can be relative (e.g.:
MyPlugin.aar) in which case it's relative to theres://android/pluginsdirectory.Der Dateipfad kann absolut sein:
res://some_path/MyPlugin.aar.If binary_type is
remote, then this should be a declaration for a remote gradle binary (e.g.:org.godot.example:my-plugin:0.0.0).Der Abschnitt
Abhängigkeitenund dessen Felder sind optional und wie folgt definiert:
local: contains a list of filepaths to the local
.aarbinary files the plugin depends on. Similarly to thebinaryfield (when thebinary_typeislocal), the local binaries' filepaths can be relative or absolute.remote: contains a list of remote binary gradle dependencies for the plugin.
custom_maven_repos: contains a list of URLs specifying the custom maven repositories required for the plugin's dependencies.
Laden und Verwenden eines Android Plugins¶
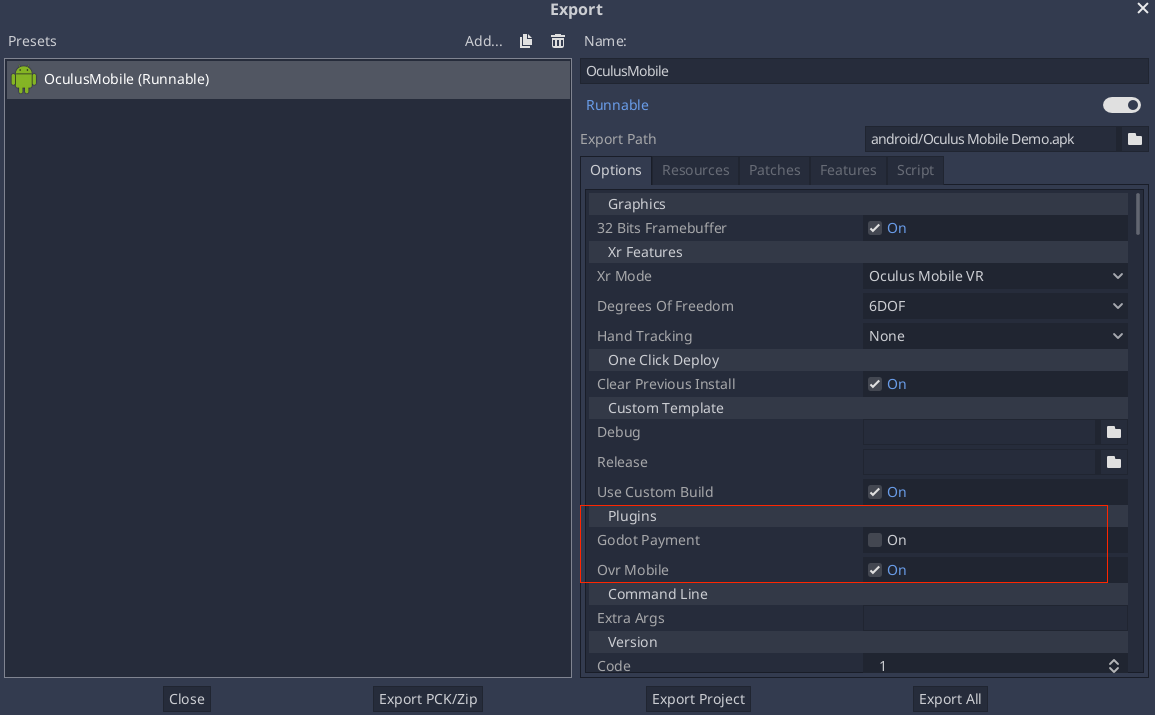
Move the plugin configuration file (e.g.: MyPlugin.gdap) and, if any, its local binary (e.g.: MyPlugin.aar) and dependencies to the Godot project's res://android/plugins directory.
The Godot editor will automatically parse all .gdap files in the res://android/plugins directory and show a list of detected and toggleable plugins in the Android export presets window under the Plugins section.
Aus Ihrem Skript:
if Engine.has_singleton("MyPlugin"):
var singleton = Engine.get_singleton("MyPlugin")
print(singleton.myPluginFunction("World"))
GDNative Ressourcen bündeln¶
An Android plugin can define and provide C/C++ GDNative resources, either to provide and/or access functionality from the game logic.
The GDNative resources can be bundled within the plugin aar file which simplifies the distribution and deployment process:
The shared libraries (
.so) for the defined GDNative libraries will be automatically bundled by theaarbuild system.Godot
*.gdnliband*.gdnsresource files must be manually defined in the pluginassetsdirectory. The recommended path for these resources relative to theassetsdirectory should be:godot/plugin/v1/[PluginName]/.
For GDNative libraries, the plugin singleton object must override the org.godotengine.godot.plugin.GodotPlugin::getPluginGDNativeLibrariesPaths() method,
and return the paths to the bundled GDNative libraries config files (*.gdnlib). The paths must be relative to the assets directory.
At runtime, the plugin will provide these paths to Godot core which will use them to load and initialize the bundled GDNative libraries.
Referenzimplementierungen¶
Fehlerbeseitigung¶
Godot stürzt beim Laden ab¶
Überprüfen Sie adb logcat auf mögliche Probleme, dann:
Check that the methods exposed by the plugin used the following Java types:
void,boolean,int,float,java.lang.String,org.godotengine.godot.Dictionary,int[],byte[],float[],java.lang.String[].Komplexere Datentypen werden derzeit nicht unterstützt.