Importing audio samples¶
Supported files¶
Godot provides two options to import your audio data: WAV and Ogg Vorbis.
Each has different advantages.
WAV files use raw data or light compression (IMA-ADPCM). They are lightweight on the CPU to play back (hundreds of simultaneous voices in this format are fine). The downside is that they take up a lot of disk space.
Ogg Vorbis files use a stronger compression that results in much smaller file size, but require significantly more processing power to play back.
Note
MP3 support is available in Godot 3.3 and later.
Here is a comparative chart.
Format |
1 second of audio |
|---|---|
WAV 24-bit, 96 kHz, stereo |
576 KB |
WAV 16-bit, 44 kHz, mono |
88 KB |
WAV 16-bit, IMA-ADPCM, mono |
22 KB |
Ogg Vorbis 128 Kb/s, stereo |
16 KB |
Ogg Vorbis 96 Kb/s, stereo |
12 KB |
Consider using WAV for short and repetitive sound effects, and Ogg Vorbis for music, speech, and long sound effects.
Best practices¶
Godot has an extensive bus system with built-in effects. This saves SFX artists the need to add reverb to the sound effects, reducing their size greatly and ensuring correct trimming. Say no to SFX with baked reverb!
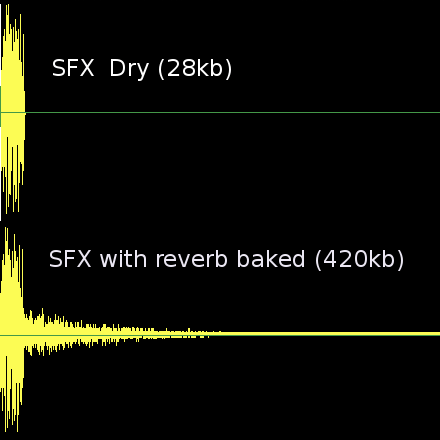
As you can see above, sound effects become huge with reverb added.
Trimming¶
One issue that happens often is that the waveform is exported with long silences at the beginning and at the end. These are inserted by DAWs when saving to a waveform, increase their size unnecessarily and add latency to the moment they are played back.
Importing as WAV with the Trimming option enabled solves this.
Looping¶
Godot supports looping in the samples (tools such as Sound Forge or Audition can add loop points to WAV files). This is useful for sound effects, such as engines, machine guns etc. Ping-pong looping is also supported.
As an alternative, the Import dock has a Loop option that enables looping for the entire sample when importing.