Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
The main game scene¶
Now it's time to bring everything we did together into a playable game scene.
Create a new scene and add a Node named Main.
(The reason we are using Node instead of Node2D is because this node will
be a container for handling game logic. It does not require 2D functionality itself.)
Click the Instance button (represented by a chain link icon) and select your saved
player.tscn.
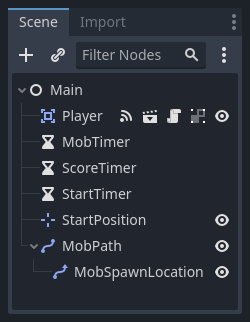
Main 의 자식으로 다음의 노드들을 추가하고, 설명대로 이름을 지으세요 (값은 초 단위입니다):
Timer (
MobTimer라고 이름지음) - 얼마나 자주 몹이 스폰하는지를 조절하기 위해 사용Timer (
ScoreTimer라고 이름지음) - 매 초마다 점수를 증가시키기 위해 사용Timer (
StratTimer라고 이름지음) - 시작하기 전에 지연시간을 주기 위해 사용Marker2D (named
StartPosition) - to indicate the player's start position
각 Timer마다 Wait Time 속성을 다음과 같이 설정하세요:
MobTimer:0.5ScoreTimer:1StartTimer:2
그리고, StartTimer 속성의 One Shot을 "사용(On)"으로 설정하고 StartPosition 노드의 Position을 (240, 450) 으로 설정하세요.
몹 스폰하기¶
메인 노드는 새로운 몹을 스폰할 것이고 우리는 몹이 화면 모서리 아무 위치에서나 나타나도록 만들고 싶습니다. Path2D 노드를 Main의 자식으로 추가하고 MobPath라고 이름지으세요. Path2D를 선택하면 편집기 위쪽에 새로운 버튼들이 나타납니다:

Select the middle one ("Add Point") and draw the path by clicking to add the points at the corners shown. To have the points snap to the grid, make sure "Use Grid Snap" and "Use Smart Snap" are both selected. These options can be found to the left of the "Lock" button, appearing as a magnet next to some dots and intersecting lines, respectively.

중요
시계 방향 으로 그리세요, 그렇지 않으면 몹들은 안쪽 이 아닌 바깥쪽 으로 향할 것입니다!

이미지에서 4개의 점을 찍고 난 후, "곡선 닫기(Close Curve)" 버튼을 누르면 곡선이 완성됩니다.
이제 경로를 정의하기 위해 PathFollow2D 노드를 MobPath의 자식으로 추가한 후 MobSpawnLocation이라고 이름지으세요. 이 노드는 자동으로 회전하고 이동하면서 경로를 따라갈 것입니다, 그러므로 경로를 따라 임의의 위치와 방향을 선택하기 위해 이것을 사용할 수 있습니다.
씬 트리는 다음과 같아야 합니다:
메인 스크립트¶
Add a script to Main. At the top of the script, we use
@export var mob_scene: PackedScene to allow us to choose the Mob scene we want
to instance.
extends Node
@export var mob_scene: PackedScene
var score
using Godot;
public partial class Main : Node
{
// Don't forget to rebuild the project so the editor knows about the new export variable.
[Export]
public PackedScene MobScene { get; set; }
private int _score;
}
Click the Main node and you will see the Mob Scene property in the Inspector
under "Script Variables".
다음 두 가지 방법으로 이 속성의 값을 할당할 수 있습니다:
Drag
mob.tscnfrom the "FileSystem" dock and drop it in the Mob Scene property.Click the down arrow next to "[empty]" and choose "Load". Select
mob.tscn.
Next, select the instance of the Player scene under Main node in the Scene dock,
and access the Node dock on the sidebar. Make sure to have the Signals tab selected
in the Node dock.
You should see a list of the signals for the Player node. Find and
double-click the hit signal in the list (or right-click it and select
"Connect..."). This will open the signal connection dialog. We want to make a
new function named game_over, which will handle what needs to happen when a
game ends. Type "game_over" in the "Receiver Method" box at the bottom of the
signal connection dialog and click "Connect". You are aiming to have the hit signal
emitted from Player and handled in the Main script. Add the following code
to the new function, as well as a new_game function that will set
everything up for a new game:
func game_over():
$ScoreTimer.stop()
$MobTimer.stop()
func new_game():
score = 0
$Player.start($StartPosition.position)
$StartTimer.start()
public void GameOver()
{
GetNode<Timer>("MobTimer").Stop();
GetNode<Timer>("ScoreTimer").Stop();
}
public void NewGame()
{
_score = 0;
var player = GetNode<Player>("Player");
var startPosition = GetNode<Marker2D>("StartPosition");
player.Start(startPosition.Position);
GetNode<Timer>("StartTimer").Start();
}
Now connect the timeout() signal of each of the Timer nodes (StartTimer,
ScoreTimer, and MobTimer) to the main script. StartTimer will start
the other two timers. ScoreTimer will increment the score by 1.
func _on_score_timer_timeout():
score += 1
func _on_start_timer_timeout():
$MobTimer.start()
$ScoreTimer.start()
private void OnScoreTimerTimeout()
{
_score++;
}
private void OnStartTimerTimeout()
{
GetNode<Timer>("MobTimer").Start();
GetNode<Timer>("ScoreTimer").Start();
}
In _on_mob_timer_timeout(), we will create a mob instance, pick a random
starting location along the Path2D, and set the mob in motion. The
PathFollow2D node will automatically rotate as it follows the path, so we
will use that to select the mob's direction as well as its position.
When we spawn a mob, we'll pick a random value between 150.0 and
250.0 for how fast each mob will move (it would be boring if they were
all moving at the same speed).
새로운 인스턴스는 add_child()를 사용해야 추가할 수 있습니다.
func _on_mob_timer_timeout():
# Create a new instance of the Mob scene.
var mob = mob_scene.instantiate()
# Choose a random location on Path2D.
var mob_spawn_location = $MobPath/MobSpawnLocation
mob_spawn_location.progress_ratio = randf()
# Set the mob's direction perpendicular to the path direction.
var direction = mob_spawn_location.rotation + PI / 2
# Set the mob's position to a random location.
mob.position = mob_spawn_location.position
# Add some randomness to the direction.
direction += randf_range(-PI / 4, PI / 4)
mob.rotation = direction
# Choose the velocity for the mob.
var velocity = Vector2(randf_range(150.0, 250.0), 0.0)
mob.linear_velocity = velocity.rotated(direction)
# Spawn the mob by adding it to the Main scene.
add_child(mob)
private void OnMobTimerTimeout()
{
// Note: Normally it is best to use explicit types rather than the `var`
// keyword. However, var is acceptable to use here because the types are
// obviously Mob and PathFollow2D, since they appear later on the line.
// Create a new instance of the Mob scene.
Mob mob = MobScene.Instantiate<Mob>();
// Choose a random location on Path2D.
var mobSpawnLocation = GetNode<PathFollow2D>("MobPath/MobSpawnLocation");
mobSpawnLocation.ProgressRatio = GD.Randf();
// Set the mob's direction perpendicular to the path direction.
float direction = mobSpawnLocation.Rotation + Mathf.Pi / 2;
// Set the mob's position to a random location.
mob.Position = mobSpawnLocation.Position;
// Add some randomness to the direction.
direction += (float)GD.RandRange(-Mathf.Pi / 4, Mathf.Pi / 4);
mob.Rotation = direction;
// Choose the velocity.
var velocity = new Vector2((float)GD.RandRange(150.0, 250.0), 0);
mob.LinearVelocity = velocity.Rotated(direction);
// Spawn the mob by adding it to the Main scene.
AddChild(mob);
}
중요
Why PI? In functions requiring angles, Godot uses radians,
not degrees. Pi represents a half turn in radians, about
3.1415 (there is also TAU which is equal to 2 * PI).
If you're more comfortable working with degrees, you'll need to
use the deg_to_rad() and rad_to_deg() functions to
convert between the two.
씬 테스트하기¶
Let's test the scene to make sure everything is working. Add this new_game
call to _ready():
func _ready():
new_game()
public override void _Ready()
{
NewGame();
}
Let's also assign Main as our "Main Scene" - the one that runs automatically
when the game launches. Press the "Play" button and select main.tscn when
prompted.
팁
If you had already set another scene as the "Main Scene", you can right
click main.tscn in the FileSystem dock and select "Set As Main Scene".
플레이어를 움직이고, 몹들이 스폰되는 것을 보고, 플레이어가 몹과 충돌할 때 사라지는 것을 볼 수 있어야 합니다.
When you're sure everything is working, remove the call to new_game() from
_ready() and replace it with pass.
What's our game lacking? Some user interface. In the next lesson, we'll add a title screen and display the player's score.