Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Compiling for Linux, *BSD¶
参考
This page describes how to compile Linux editor and export template binaries from source. If you're looking to export your project to Linux instead, read Exporting for Linux.
必要条件¶
Linux またはその他の Unix バリアントでコンパイルするには、次のことが必要です:
GCC 7以降 または Clang 6以降。
3.0以降のSCons ビルドシステム。
注釈
If your distribution uses Python 2 by default, or you are using a version of SCons prior to 3.1.2, you will need to change the version of Python that SCons uses by changing the shebang (the first line) of the SCons script file to
#! /usr/bin/python3. Use the commandwhich sconsto find the location of the SCons script file.pkg-config (used to detect the development libraries listed below).
Development libraries:
X11, Xcursor, Xinerama, Xi and XRandR.
MesaGL.
ALSA.
PulseAudio.
任意 - libudev (
udev=yesでのビルドに)。
参考
To get the Godot source code for compiling, see ソースの取得.
Godotにおける基本的なSconsの使い方については、ビルドシステムの説明を参照してください。
ディストリビューション固有のワンライナー¶
apk add \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
g++ \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev \
mesa-dev \
libexecinfo-dev \
eudev-dev \
alsa-lib-dev \
pulseaudio-dev
pacman -S --needed \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
libxcursor \
libxinerama \
libxi \
libxrandr \
mesa \
glu \
libglvnd \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
apt-get install \
build-essential \
scons \
pkg-config \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libgl1-mesa-dev \
libglu-dev \
libasound2-dev \
libpulse-dev \
libudev-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev
dnf install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
mesa-libGL-devel \
mesa-libGLU-devel \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-libs-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libstdc++-static \
libatomic-static
pkg install \
py37-scons \
pkgconf \
xorg-libraries \
libXcursor \
libXrandr \
libXi \
xorgproto libGLU \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
emerge -an \
dev-util/scons \
x11-libs/libX11 \
x11-libs/libXcursor \
x11-libs/libXinerama \
x11-libs/libXi \
media-libs/mesa \
media-libs/glu \
media-libs/alsa-lib \
media-sound/pulseaudio
urpmi \
scons \
task-c++-devel \
pkgconfig \
"pkgconfig(alsa)" \
"pkgconfig(glu)" \
"pkgconfig(libpulse)" \
"pkgconfig(udev)" \
"pkgconfig(x11)" \
"pkgconfig(xcursor)" \
"pkgconfig(xinerama)" \
"pkgconfig(xi)" \
"pkgconfig(xrandr)"
pkg_add \
python \
scons \
llvm
zypper install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
Mesa-libGL-devel \
alsa-devel \
libpulse-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libGLU1
pkg_add \
pkg-config \
py37-scons
ヒント
For audio support, you can optionally install pulseaudio.
eopkg install -c \
system.devel \
scons \
libxcursor-devel \
libxinerama-devel \
libxi-devel \
libxrandr-devel \
mesalib-devel \
libglu \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-devel
コンパイル¶
ターミナルを起動し、エンジンソースコードのルートディレクトリに移動し、次のように入力します:
scons platform=linuxbsd
注釈
Prior to Godot 4.0, the Linux/*BSD target was called x11 instead of
linuxbsd. If you are looking to compile Godot 3.x, make sure to use the
3.x branch of this documentation.
If all goes well, the resulting binary executable will be placed in the "bin" subdirectory. This executable file contains the whole engine and runs without any dependencies. Executing it will bring up the Project Manager.
注釈
GCCではなくClangを使用してコンパイルする場合は、次のコマンドを使用します:
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes
Clangを使うことはOpenBSDの要件のようで、そうしないとフォントが作れません。
注釈
If you are compiling Godot for production use, then you can
make the final executable smaller and faster by adding the
SCons options target=template_release production=yes.
If you are compiling Godot with GCC, you can make the binary
even smaller and faster by adding the SCons option lto=full.
As link-time optimization is a memory-intensive process,
this will require about 7 GB of available RAM while compiling.
注釈
If you want to use separate editor settings for your own Godot builds
and official releases, you can enable
自己完結型モード by creating a file called
._sc_ or _sc_ in the bin/ folder.
Running a headless/server build¶
To run in headless mode which provides editor functionality to export projects in an automated manner, use the normal build:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=editor
And then use the --headless command line argument:
./bin/godot.linuxbsd.editor.x86_64 --headless
To compile a debug server build which can be used with remote debugging tools, use:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug
To compile a server build which is optimized to run dedicated game servers, use:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release production=yes
エクスポートテンプレートの構築¶
警告
Linuxのバイナリは通常、ビルドしたディストリビューションより古いディストリビューションでは動きません。もし大抵のディストリビューションで動作するバイナリを配布したいなら、Ubuntu 16.04のような古いディストリビューションでビルドするべきでしょう。バーチャルマシンやコンテナを使えば、適切なビルド環境をセットアップできます。
To build Linux or *BSD export templates, run the build system with the following parameters:
(32ビット)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_32
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_32
(64ビット)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_64
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_64
注意点として、現在のホスト プラットフォームの反対のビット(64/32)へのクロスコンパイルは、簡単にいくとは限らず、chroot環境が必要になるかもしれません。
To create standard export templates, the resulting files in the bin/ folder
must be copied to:
$HOME/.local/share/godot/export_templates/<version>/
and named like this (even for *BSD which is seen as "Linux/X11" by Godot):
linux_x11_32_debug
linux_x11_32_release
linux_x11_64_debug
linux_x11_64_release
ただし、カスタムモジュールまたはカスタムC++ コードを作成する場合は、ここでカスタムエクスポート テンプレートとしてバイナリを構成する必要があります:
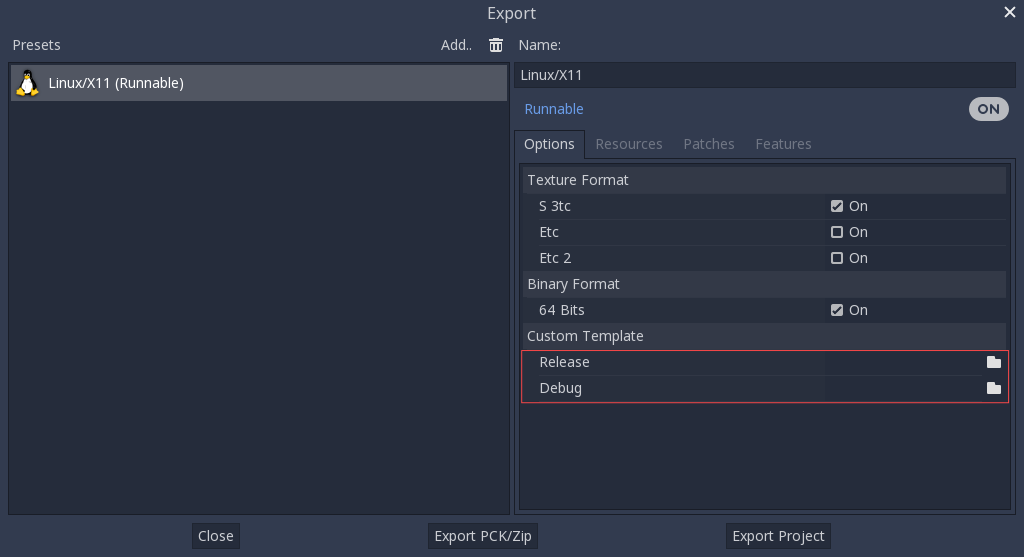
この場合はコピーする必要はなく、Godotのソースフォルダ内にある bin\ ディレクトリに出力されたファイルを指定するだけです。こうすれば、次にビルドした時も、自動的にカスタム テンプレートを参照するようになります。
ClangとLLDを使用して開発を高速化する¶
ClangとLLDを使用してGodotを構築することもできます。これには、デフォルトのGCC + GNU ldセットアップと比較して2つの利点があります:
LLDは、GNU ldまたはgoldと比較してGodotを大幅に高速にリンクします。これにより、反復時間が短縮されます。
Clangは、GCCよりも有用なエラーメッセージを提供する傾向があります。
これを行うには、ディストリビューションのパッケージマネージャーからClangと lld パッケージをインストールし、次のSConsコマンドを使用します:
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes linker=lld
After the build is completed, a new binary with a .llvm suffix will be
created in the bin/ folder.
リンク時最適化を使用してコンパイルし、結果のバイナリをより小さく、より高速にすることができるため、プロダクションビルドにはGCCを使用することをお勧めします。
If this error occurs:
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l:libatomic.a: No such file or directory
There are two solutions:
In your SCons command, add the parameter
use_static_cpp=no.Follow these instructions to configure, build, and install
libatomic_ops. Then, copy/usr/lib/libatomic_ops.ato/usr/lib/libatomic.a, or create a soft link tolibatomic_opsby commandln -s /usr/lib/libatomic_ops.a /usr/lib/libatomic.a. The soft link can ensure the latestlibatomic_opswill be used without the need to copy it everytime when it is updated.
Using mold for faster development¶
For even faster linking compared to LLD, you can use mold. mold can be used with either GCC or Clang.
As of January 2023, mold is not readily available in Linux distribution repositories, so you will have to install its binaries manually.
Download mold binaries from its releases page.
Extract the
.tar.gzfile, then move the extraced folder to a location such as.local/share/mold.Add
$HOME/.local/share/mold/binto your user'sPATHenvironment variable. For example, you can add the following line at the end of your$HOME/.bash_profilefile:
PATH="$HOME/.local/share/mold/bin:$PATH"
Open a new terminal (or run
source "$HOME/.bash_profile"), then use the following SCons command when compiling Godot:scons platform=linuxbsd linker=mold
Using system libraries for faster development¶
Godot bundles the source code of various third-party libraries. You can choose to use system versions of third-party libraries instead. This makes the Godot binary faster to link, as third-party libraries are dynamically linked. Therefore, they don't need to be statically linked every time you build the engine (even on small incremental changes).
However, not all Linux distributions have packages for third-party libraries available (or they may not be up-to-date).
Moving to system libraries can reduce linking times by several seconds on slow CPUs, but it requires manual testing depending on your Linux distribution. Also, you may not be able to use system libraries for everything due to bugs in the system library packages (or in the build system, as this feature is less tested).
To compile Godot with system libraries, install these dependencies on top of the ones listed in the ディストリビューション固有のワンライナー:
Fedora |
sudo dnf install embree3-devel enet-devel glslang-devel graphite2-devel harfbuzz-devel libicu-devel \
libsquish-devel libtheora-devel libvorbis-devel libwebp-devel libzstd-devel mbedtls-devel \
miniupnpc-devel
|
After installing all required packages, use the following command to build Godot:
scons platform=linuxbsd builtin_embree=no builtin_enet=no builtin_freetype=no builtin_graphite=no builtin_harfbuzz=no builtin_libogg=no builtin_libpng=no builtin_libtheora=no builtin_libvorbis=no builtin_libwebp=no builtin_mbedtls=no builtin_miniupnpc=no builtin_pcre2=no builtin_zlib=no builtin_zstd=no
You can view a list of all built-in libraries that have system alternatives by
running scons -h, then looking for options starting with builtin_.
警告
When using system libraries, the resulting library is not portable across Linux distributions anymore. Do not use this approach for creating binaries you intend to distribute to others, unless you're creating a package for a Linux distribution.
Using Pyston for faster development¶
You can use Pyston to run SCons. Pyston is a JIT-enabled implementation of the Python language (which SCons is written in). It is currently only compatible with Linux. Pyston can speed up incremental builds significantly, often by a factor between 1.5× and 2×. Pyston can be combined with Clang and LLD to get even faster builds.
Download the latest portable Pyston release.
Extract the portable
.tar.gzto a set location, such as$HOME/.local/opt/pyston/(create folders as needed).Use
cdto reach the extracted Pyston folder from a terminal, then run./pyston -m pip install sconsto install SCons within Pyston.To make SCons via Pyston easier to run, create a symbolic link of its wrapper script to a location in your
PATHenvironment variable:ln -s ~/.local/opt/pyston/bin/scons ~/.local/bin/pyston-scons
Instead of running
scons <build arguments>, runpyston-scons <build arguments>to compile Godot.
If you can't run pyston-scons after creating the symbolic link,
make sure $HOME/.local/bin/ is part of your user's PATH environment variable.
注釈
Alternatively, you can run python -m pip install pyston_lite_autoload
then run SCons as usual. This will automatically load a subset of Pyston's
optimizations in any Python program you run. However, this won't bring as
much of a performance improvement compared to installing "full" Pyston.