Playing videos¶
Godot supports video playback with the VideoPlayer node.
Supported playback formats¶
The only supported format in core is Ogg Theora (not to be confused with Ogg Vorbis audio). It's possible for extensions to bring support for additional formats, but no such extensions exist yet as of July 2022.
H.264 and H.265 cannot be supported in core Godot, as they are both encumbered by software patents. AV1 is royalty-free, but it remains slow to decode on the CPU and hardware decoding support isn't readily available on all GPUs in use yet.
WebM is supported in core in Godot 3.x, but support for it will be removed in 4.0 as it proved to be too buggy and difficult to maintain. Therefore, using WebM is not recommended.
Note
You may find videos with an .ogg or .ogx extensions, which are generic
extensions for data within an Ogg container.
Renaming these file extensions to .ogv may allow the videos to be
imported in Godot. However, not all files with .ogg or .ogx
extensions are videos - some of them may only contain audio.
Setting up VideoPlayer¶
Create a VideoPlayer node using the Create New Node dialog.
Select the VideoPlayer node in the scene tree dock, go to the inspector and load an
.ogvfile in the Stream property.If you don't have your video in Ogg Theora format yet, jump to Recommended Theora encoding settings.
If you want the video to play as soon as the scene is loaded, check Autoplay in the inspector. If not, leave Autoplay disabled and call
play()on the VideoPlayer node in a script to start playback when desired.
Handling resizing and different aspect ratios¶
By default in Godot 4.0, the VideoPlayer will automatically be resized to match the video's resolution. You can make it follow usual Control sizing by enabling Expand on the VideoPlayer node.
To adjust how the VideoPlayer node resizes depending on window size, adjust the anchors using the Layout menu at the top of the 2D editor viewport. However, this setup may not be powerful enough to handle all use cases, such as playing fullscreen videos without distorting the video (but with empty space on the edges instead). For more control, you can use an AspectRatioContainer node, which is designed to handle this kind of use case:
Add an AspectRatioContainer node. Make sure it is not a child of any other container node. Select the AspectRatioContainer node, then set its Layout at the top of the 2D editor to Full Rect. Set Ratio in the AspectRatioContainer node to match your video's aspect ratio. You can use math formulas in the inspector to help yourself. Remember to make one of the operands a float. Otherwise, the division's result will always be an integer.
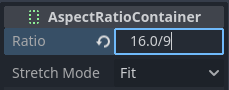
This will evaluate to (approximately) 1.777778¶
Once you've configured the AspectRatioContainer, reparent your VideoPlayer node to be a child of the AspectRatioContainer node. Make sure Expand is disabled on the VideoPlayer. Your video should now scale automatically to fit the whole screen while avoiding distortion.
See also
See Multiple resolutions for more tips on supporting multiple aspect ratios in your project.
Displaying a video on a 3D surface¶
Using a VideoPlayer node as a child of a Viewport node, it's possible to display any 2D node on a 3D surface. For example, this can be used to display animated billboards when frame-by-frame animation would require too much memory.
This can be done with the following steps:
Create a Viewport node. Set its size to match your video's size in pixels.
Create a VideoPlayer node as a child of the Viewport node and specify a video path in it. Make sure Expand is disabled, and enable Autoplay if needed.
Create a MeshInstance node with a PlaneMesh or QuadMesh resource in its Mesh property. Resize the mesh to match the video's aspect ratio (otherwise, it will appear distorted).
Create a new SpatialMaterial resource in the Material Override property in the GeometryInstance section.
Enable Local To Scene in the SpatialMaterial's Resource section (at the bottom). This is required before you can use a ViewportTexture in its Albedo Texture property.
In the SpatialMaterial, set the Albedo > Texture property to New ViewportTexture. Edit the new resource by clicking it, then specify the path to the Viewport node in the Viewport Path property.
Enable Albedo Tex Force sRGB in the SpatialMaterial to prevent colors from being washed out.
If the billboard is supposed to emit its own light, enable Flags > Unshaded to improve rendering performance.
See Using Viewports and the GUI in 3D demo for more information on setting this up.
Video decoding conditions and recommended resolutions¶
Video decoding is performed on the CPU, as GPUs don't have hardware acceleration for decoding Theora videos. Modern desktop CPUs can decode Ogg Theora videos at 1440p @ 60 FPS or more, but low-end mobile CPUs will likely struggle with high-resolution videos.
To ensure your videos decode smoothly on varied hardware:
When developing games for desktop platforms, it's recommended to encode in 1080p at most (preferably at 30 FPS). Most people are still using 1080p or lower resolution displays, so encoding higher-resolution videos may not be worth the increased file size and CPU requirements.
When developing games for mobile or web platforms, it's recommended to encode in 720p at most (preferably at 30 FPS or even lower). The visual difference between 720p and 1080p videos on a mobile device is usually not that noticeable.
Playback limitations¶
There are several limitations with the current implementation of video playback in Godot:
Seeking a video to a certain point is not supported.
Changing playback speed is not supported. VideoPlayer also won't follow Engine.time_scale.
Looping is not supported, but you can connect a VideoPlayer's finished signal to a function that plays the video again. However, this will cause a black frame to be visible when the video restarts. This can be worked around by adding a fade to black in the video file before the video ends, or by hiding the video for one frame and displaying a TextureRect with a screenshot of the first frame of the video until the video is restarted.
Streaming a video from a URL is not supported.
Recommended Theora encoding settings¶
A word of advice is to avoid relying on built-in Ogg Theora exporters (most of the time). There are 2 reasons you may want to favor using an external program to encode your video:
Some programs such as Blender can render to Ogg Theora. However, the default quality presets are usually very low by today's standards. You may be able to increase the quality options in the software you're using, but you may find the output quality to remain less than ideal (given the increased file size). This usually means that the software only supports encoding to constant bit rate (CBR), instead of variable bit rate (VBR). VBR encoding should be preferred in most scenarios as it provides a better quality to file size ratio.
Some other programs can't render to Ogg Theora at all.
In this case, you can render the video to an intermediate high-quality format (such as a high-bitrate H.264 video) then re-encode it to Ogg Theora. Ideally, you should use a lossless or uncompressed format as an intermediate format to maximize the quality of the output Ogg Theora video, but this can require a lot of disk space.
HandBrake (GUI) and FFmpeg (CLI) are popular open source tools for this purpose. FFmpeg has a steeper learning curve, but it's more powerful.
Here are example FFmpeg commands to convert a MP4 video to Ogg Theora. Since FFmpeg supports a lot of input formats, you should be able to use the commands below with almost any input video format (AVI, MOV, WebM, …).
Note
Make sure your copy of FFmpeg is compiled with libtheora and libvorbis support.
You can check this by running ffmpeg without any arguments, then looking
at the configuration: line in the command output.
Balancing quality and file size¶
The video quality level (-q:v) must be between 1 and 10. Quality
6 is a good compromise between quality and file size. If encoding at a high
resolution (such as 1440p or 4K), you will probably want to decrease -q:v to
5 to keep file sizes reasonable. Since pixel density is higher on a 1440p or
4K video, lower quality presets at higher resolutions will look as good or
better compared to low-resolution videos.
The audio quality level (-q:a) must be between -1 and 10. Quality
6 provides a good compromise between quality and file size. In contrast to
video quality, increasing audio quality doesn't increase the output file size
nearly as much. Therefore, if you want the cleanest audio possible, you can
increase this to 9 to get perceptually lossless audio. This is especially
valuable if your input file already uses lossy audio compression. See
this page
for a table listing Ogg Vorbis audio quality presets and their respective
variable bitrates.
FFmpeg: Convert while preserving original video resolution¶
The following command converts the video while keeping its original resolution. The video and audio's bitrate will be variable to maximize quality while saving space in parts of the video/audio that don't require a high bitrate (such as static scenes).
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -q:v 6 -q:a 6 output.ogv
FFmpeg: Resize the video then convert it¶
The following command resizes a video to be 720 pixels tall (720p), while preserving its existing aspect ratio. This helps decrease the file size significantly if the source is recorded at a higher resolution than 720p:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "scale=-1:720" -q:v 6 -q:a 6 output.ogv