Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Standard Material 3D and ORM Material 3D¶
はじめに¶
StandardMaterial3D and ORMMaterial3D (Occlusion, Roughness, Metallic)
are default 3D materials that aim to provide most of the features artists look
for in a material, without the need for writing shader code. However, they can
be converted to shader code if additional functionality is needed.
This tutorial explains the parameters present in both materials.
There are 4 ways to add these materials to an object. A material can be added in the Material property of the mesh. It can be added in the Material property of the node using the mesh (such as a MeshInstance3D node), the Material Override property of the node using the mesh, and the Material Overlay.
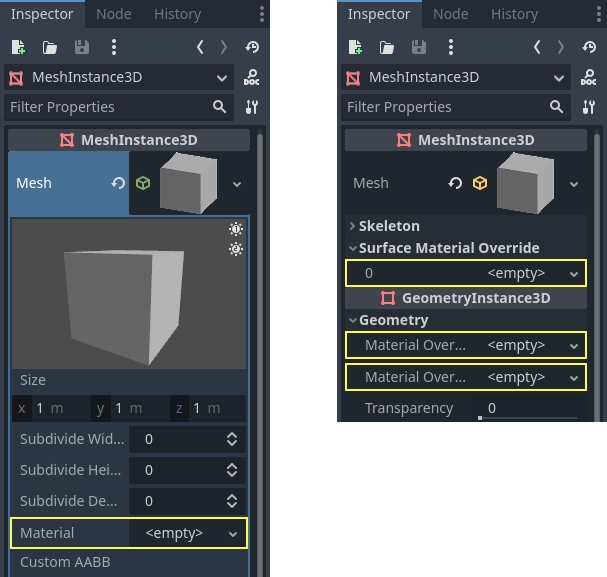
メッシュ自体にマテリアルを追加すると、そのメッシュが使用されるたびにそのマテリアルが追加されます。メッシュを使用してノードにマテリアルを追加すると、マテリアルはそのノードでのみ使用され、メッシュのマテリアルプロパティもオーバーライドします。マテリアルがノードの Material Override プロパティに追加された場合、そのノードでのみ使用されます。また、ノードの通常のマテリアルプロパティとメッシュのマテリアルプロパティもオーバーライドします。
The Material Overlay property will render a material over the current one being used by the mesh. As an example, this can be used to put a transparent shield effect on a mesh.
BaseMaterial 3D settings¶
StandardMaterial3D has many settings that determine the look of a material. All of these are under the BaseMaterial3D category

ORM materials are almost exactly the same with one difference. Instead of separate settings and textures for occlusion, roughness, and metallic, there is a single ORM texture. The different color channels of that texture are used for each parameter. Programs such as Substance Painter and Armor Paint will give you the option to export in this format, for these two programs it's with the export preset for unreal engine, which also uses ORM textures.
Transparency¶
By default, materials in Godot are opaque. This is fast to render, but it means the material can't be seen through even if you use a transparent texture in the Albedo > Texture property (or set Albedo > Color to a transparent color).
To be able to see through a material, the material needs to be made transparent. Godot offers several transparency modes:
Disabled: Material is opaque. This is the fastest to render, with all rendering features supported.
Alpha: Material is transparent. Semi-transparent areas are drawn with blending. This is slow to render, but it allows for partial transparency (also known as translucency). Materials using alpha blending also can't cast shadows, and are not visible in screen-space reflections.
Alpha is a good fit for particle effects and VFX.
Alpha Scissor: Material is transparent. Semi-transparent areas whose opacity is below Alpha Scissor Threshold are not drawn (above this opacity, these are drawn as opaque). This is faster to render than Alpha and doesn't exhibit transparency sorting issues. The downside is that this results in "all or nothing" transparency, with no intermediate values possible. Materials using alpha scissor can cast shadows.
Alpha Scissor is ideal for foliage and fences, since these have hard edges and require correct sorting to look good.
Alpha Hash: Material is transparent. Semi-transparent areas are drawn using dithering. This is also "all or nothing" transparency, but dithering helps represent partially opaque areas with limited precision depending on viewport resolution. Materials using alpha hash can cast shadows.
Alpha Hash is suited for realistic-looking hair, although stylized hair may work better with alpha scissor.
Depth Pre-Pass: This renders the object's fully opaque pixels via the opaque pipeline first, then renders the rest with alpha blending. This allows transparency sorting to be mostly correct (albeit not fully so, as partially transparent regions may still exhibit incorrect sorting). Materials using depth prepass can cast shadows.
注釈
Godot will automatically force the material to be transparent with alpha blending if any of these conditions is met:
Setting the transparency mode to Alpha (as described here).
Setting a blend mode other than the default Mix
Enabling Refraction, Proximity Fade, or Distance Fade.
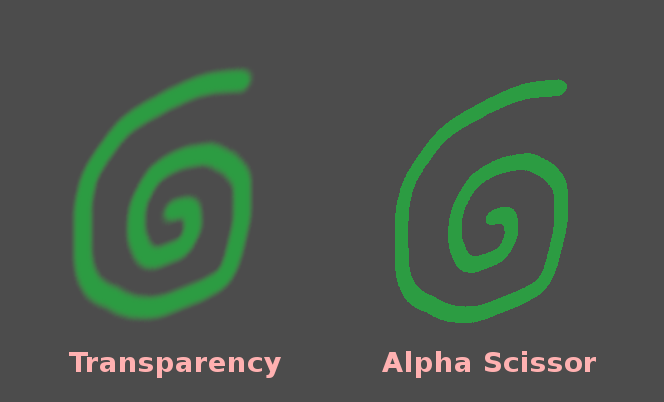
Comparison between alpha blending (left) and alpha scissor (right) transparency:

警告
Alpha-blended transparency has several limitations:
Alpha-blended materials are significantly slower to render, especially if they overlap.
Alpha-blended materials may exhibit sorting issues when transparent surfaces overlap each other. This means that surfaces may render in the incorrect order, with surfaces in the back appearing to be in front of those which are actually closer to the camera.
Alpha-blended materials don't cast shadows, although they can receive shadows.
Alpha-blended materials don't appear in any reflections (other than reflection probes).
Screen-space reflections and sharp SDFGI reflections don't appear on alpha-blended materials. When SDFGI is enabled, rough reflections are used as a fallback regardless of material roughness.
Before using the Alpha transparency mode, always consider whether another transparency mode is more suited for your needs.
Alpha Antialiasing¶
注釈
This property is only visible when the transparency mode is Alpha Scissor or Alpha Hash.
While alpha scissor and alpha hash materials are faster to render than alpha-blended materials, they exhibit hard edges between opaque and transparent regions. While it's possible to use post-processing-based antialiasing techniques such as FXAA and TAA, this is not always desired as these techniques tend to make the final result look blurrier or exhibit ghosting artifacts.
There are 3 alpha antialiasing modes available:
Disabled: No alpha antialiasing. Edges of transparent materials will appear aliased unless a post-processing-based antialiasing solution is used.
Alpha Edge Blend: Results in a smooth transition between opaque and transparent areas. Also known as "alpha to coverage".
Alpha Edge Clip: Results in a sharp, but still antialiased transition between opaque and transparent areas. Also known as "alpha to coverage + alpha to one".
When the alpha antialiasing mode is set to Alpha Edge Blend or Alpha Edge
Clip, a new Alpha Antialiasing Edge property becomes visible below in the
inspector. This property controls the threshold below which pixels should be
made transparent. While you've already defined an alpha scissor threshold (when
using Alpha Scissor only), this additional threshold is used to smoothly
transition between opaque and transparent pixels. Alpha Antialiasing Edge
must always be set to a value that is strictly below the alpha scissor
threshold. The default of 0.3 is a sensible value with an alpha scissor of
threshold of 0.5, but remember to adjust this alpha antialiasing edge when
modifying the alpha scissor threshold.
If you find the antialiasing effect not effective enough, try increasing Alpha Antialiasing Edge while making sure it's below Alpha Scissor Threshold (if the material uses alpha scissor). On the other hand, if you notice the texture's appearance visibly changing as the camera moves closer to the material, try decreasing Alpha Antialiasing Edge.
重要
For best results, MSAA 3D should be set to at least 2× in the Project Settings when using alpha antialiasing. This is because this feature relies on alpha to coverage, which is a feature provided by MSAA.
Without MSAA, a fixed dithering pattern is applied on the material's edges, which isn't very effective at smoothing out edges (although it can still help a little).
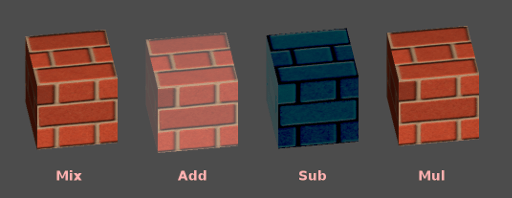
ブレンドモード¶
マテリアルのブレンドモードをコントロールします。Mix 以外のモードでは、オブジェクトが強制的に透過パイプラインをスルーする(処理されない)ことに注意してください。
Mix: デフォルトのブレンドモード、アルファはオブジェクトの表示量(透け方)を制御します。
Add: The final color of the object is added to the color of the screen, nice for flares or some fire-like effects.
Sub: The final color of the object is subtracted from the color of the screen.
Mul: The final color of the object is multiplied with the color of the screen.
カリングモード¶
背面がレンダリングされるときにオブジェクトのどちら側が描画されないかを決定します:
Back: オブジェクトの背面は、表示されていないときにカリングされます(デフォルト)。
Front: 表示されていない場合、オブジェクトの前面がカリングされます。
Disabled: 両面オブジェクトに使用します(カリングは実行されません)。
注釈
By default, Blender has backface culling disabled on materials and will export materials to match how they render in Blender. This means that materials in Godot will have their cull mode set to Disabled. This can decrease performance since backfaces will be rendered, even when they are being culled by other faces. To resolve this, enable Backface Culling in Blender's Materials tab, then export the scene to glTF again.
Depth Draw Mode(深度描画モード)¶
深度レンダリングを実行する必要がある場合を指定します。
Opaque Only(デフォルト): 深度(奥行き)は不透明オブジェクトに対してのみ描画されます。
Always: 不透明オブジェクトと透明オブジェクトの両方に対して深度描画が描画されます。
Never: No depth draw takes place (do not confuse this with the No Depth Test option below).
Depth Pre-Pass: 透明なオブジェクトの場合、まず不透明な部分で不透明なパスが作成され、次に透明度が上に描画されます。このオプションは、透明な草や木の葉で使用します。

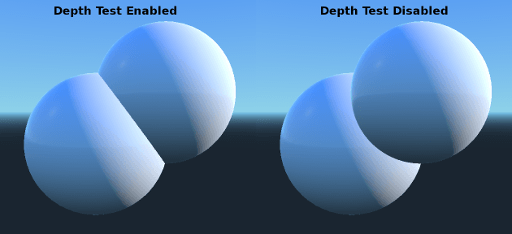
No Depth Test(深度テスト無し)¶
近くのオブジェクトを遠くのオブジェクトの上に表示するために、深度テストが実行されます。無効にすると、オブジェクトが他のすべての上(または下)に表示されます。
これを無効にすることは、ワールド空間でインジケータを描画する場合に最適で、Materialの Render Priority プロパティともに非常にうまく機能します(このページの下部を参照)。
シェーディング¶
Shading mode¶
Godotでは深度プリパスのおかげで、ピクセルあたりのコストはほぼ均一です。すべての照明計算は、すべてのピクセルで照明シェーダーを実行することによって行われます。
これらの計算にはコストがかかるため、いくつもの透明度を持つレイヤーを描画する場合などの、一部のコーナーケース(極まれで厄介なケース)ではパフォーマンスが大幅に低下する可能性があります(これはパーティクルシステムでは一般的です)。これらの場合、頂点ごとの照明に切り替えると役立つ場合があります。
さらに、ローエンドまたはモバイルデバイスでは、頂点照明(vertex lighting)に切り替えると、レンダリングパフォーマンスが大幅に向上します。
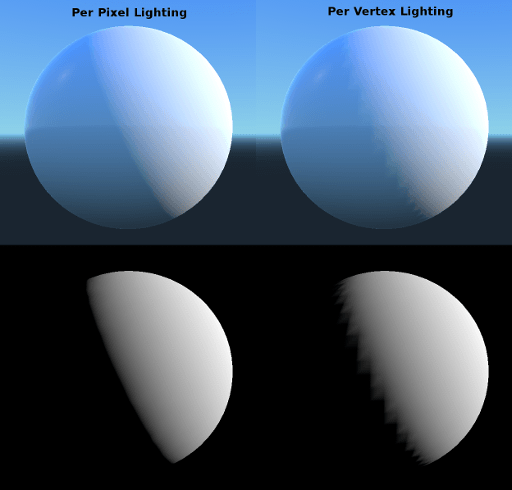
vertex lightingを有効にすると、指向性のライティングのみが影を生成できることに注意してください(パフォーマンス上の理由から)。
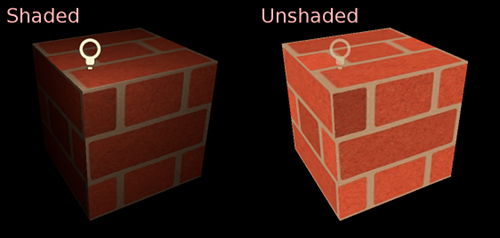
However, in some cases you might want to show just the albedo (color) and ignore the rest. To do this you can set the shading mode to unshaded
Diffuse Mode(拡散モード)¶
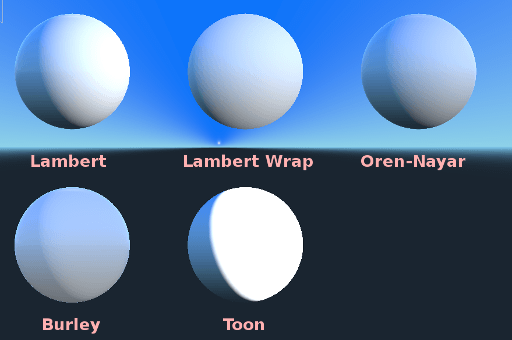
光がオブジェクトに当たるときの拡散散乱で使用されるアルゴリズムを指定します。デフォルトは Burley です。他のモードも利用可能です:
Burley: デフォルトモード、オリジナルのDisney Principled PBS拡散アルゴリズム。
Lambert: roughnessの影響を受けません。
Lambert Wrap: roughnessが増すと、Lambertを90度以上に広げます。髪の毛や低コストのサブサーフェススキャッタリングのシミュレーションに最適です。この実装は省エネルギーです。
Oren Nayar: この実装は、(roughnessによる)マイクロサーフェシングを考慮することを目的としています。粘土のような素材やある種の布に適しています。
Toon: Provides a hard cut for lighting, with smoothing affected by roughness. It is recommended you disable sky contribution from your environment's ambient light settings or disable ambient light in the StandardMaterial3D to achieve a better effect.
Specular Mode(鏡面反射モード )¶
鏡面反射(スペキュラ)blob のレンダリング方法を指定します。鏡面反射blobは、オブジェクトに反射される光源の形状を表します。
SchlickGGX: The most common blob used by PBR 3D engines nowadays.
Blinn: 前世代のエンジンで一般的。現在使用する価値はありませんが、互換性のためにここに残しました。
Phong: 上記と同じ。
Toon: トゥーンblobを作成します。これは、roughnessに応じてサイズを変更します。
Disabled: 時々blobが邪魔になります。なので立ち去りなさい!

Disable Ambient Light(アンビエントライト無効)¶
他のライトが無い場合でも照明を行うアンビエントライトをオブジェクトが受けないようにします。
Disable Fog¶
Makes the object unaffected by depth-based or volumetric fog. This is useful for particles or other additively blended materials that would otherwise show the shape of the mesh (even in places where it would be invisible without the fog).
Vertex Color(頂点色)¶
This setting allows choosing what is done by default to vertex colors that come from your 3D modeling application. By default, they are ignored.
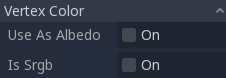
Use as Albedo(アルベドとして使用)¶
このオプションを選択すると、頂点色がアルベド色として使用されます。
Is sRGB(これはsRGBです)¶
Most 3D modeling software will likely export vertex colors as sRGB, so toggling this option on will help them look correct.
Albedo(アルベド)¶
Albedo は、他のすべての設定に関連するマテリアルのベースカラーです。Unshaded に設定すると、これが表示される唯一の色になります。 Godotの以前のバージョンでは、このチャネルの名前は Diffuse でした。名前の変更を行った主な理由は、PBR(Physically Based Rendering)では、この色が単なる拡散照明パスよりも多くの計算に影響するためです。
アルベドの色とテクスチャは、乗算されて一緒に使用されます。
アルベド色とテクスチャの アルファチャンネル は、オブジェクトの透明度にも使用されます。色またはテクスチャで アルファチャンネル を使用する場合は、transparencyを有効にするか、*alpha scissoring* を有効にしてください。
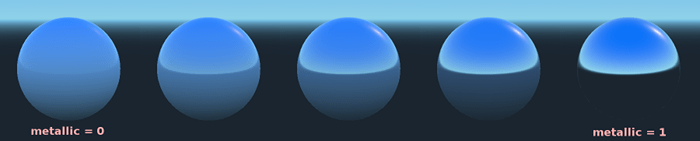
Metallic(メタリック)¶
Godotは、そのシンプルさから、競合する他のモデルではなくMetalicモデルを使用しています。このパラメーターは、マテリアルの反射率を定義します。反射が多いほど、拡散光や周囲光が材料に影響を及ぼし、反射光が多くなります。このモデルは「省エネルギー」だといわれています。
Specular パラメーターは、反射率の一般的な量です(Metallic とは異なり、これはエネルギーを節約しませんので、0.5 のままにして、必要でない限り触れないでください)。
最小の内部反射率は 0.04 であるため、現実の世界のようにマテリアルを完全に無反射にすることはできません。
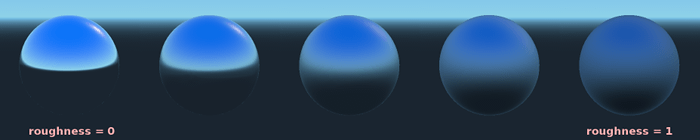
ラフネス¶
Roughness は反射の発生方法に影響します。0 の値は完璧な鏡になり、1 の値は反射を完全にぼかします(自然なマイクロサーフェシングをシミュレートします)。最も一般的な種類のマテリアルは、Metaric と Roughness の適切な組み合わせで実現できます。
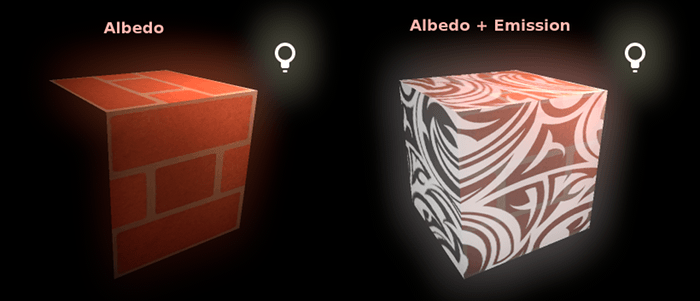
Emission(発光)¶
Emission specifies how much light is emitted by the material (keep in mind this does not include light surrounding geometry unless VoxelGI or SDFGI are used). This value is added to the resulting final image and is not affected by other lighting in the scene.
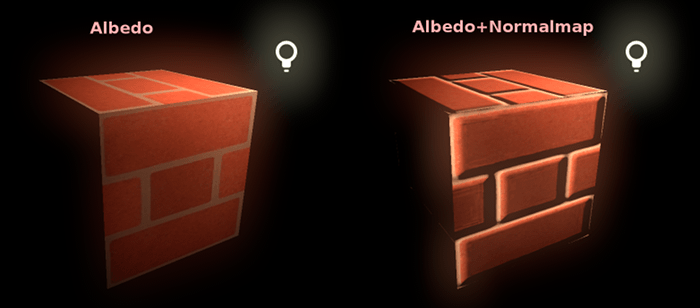
Normal map¶
Normal mapping allows you to set a texture that represents finer shape detail. This does not modify geometry, only the incident angle for light. In Godot, only the red and green channels of normal maps are used for better compression and wider compatibility.
注釈
Godot requires the normal map to use the X+, Y+ and Z+ coordinates, this is known as OpenGL style. If you've imported a material made to be used with another engine it may be DirectX style, in which case the normal map needs to be converted so its Y axis is flipped.
More information about normal maps (including a coordinate order table for popular engines) can be found here.
Rim(縁)¶
一部の布地には、周囲に光を散乱させる小さなマイクロファーがあります。 Godotは、これを Rim パラメーターでエミュレートします。Emissionチャネルのみを使用する他のリム照明の実装とは異なり、この実装では実際に光が考慮されます(光がない場合はリムが現れないことを意味します)。これにより、より真実味を作り出す効果がえられます。
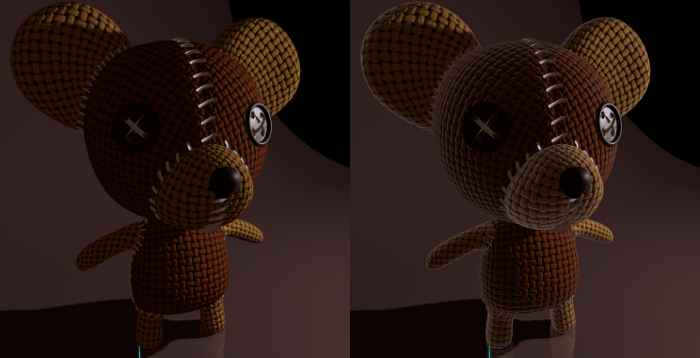
リムのサイズはroughnessに依存し、色の付け方を指定する特別なパラメーターがあります。Tint*が ``0`` の場合、ライトの色がリムに使用されます。*Tint が 1 の場合、素材のアルベドが使用されます。通常、中間値を使用するのが最適です。
Clearcoat(クリアコート)¶
Clearcoat パラメーターは、透明なコーティングの2次パスをマテリアルに追加するために使用されます。これは、車の塗装やおもちゃでは一般的です。実際には、既存のマテリアルの上に追加される小さなスペキュラblobです。

Anisotropy(異方性)¶
これにより、スペキュラblobの形状が変更され、接線空間に位置合わせされます。異方性は一般に髪の毛に使用されるか、ブラシをかけられたアルミニウムなどの素材をよりリアルにするために使用されます。フローマップ(flowmap)と組み合わせると、特にうまく機能します。

アンビエントオクルージョン¶
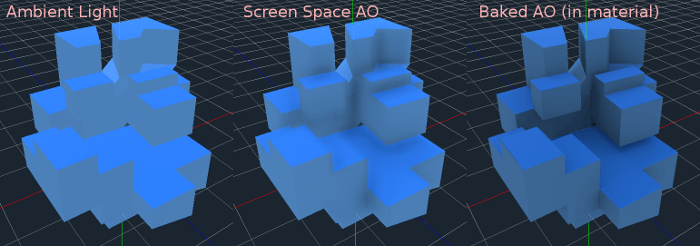
焼き込み(ベイク)処理されたアンビエントオクルージョンマップを指定することができます。このマップは、オブジェクトの各表面に到達する環境光の光量に影響します(デフォルトでは、直接光には影響しません)。スクリーンスペースアンビエントオクルージョン(SSAO)を使用してアンビエントオクルージョンを生成することは可能ですが、よく焼き込まれたAOマップの品質に勝るものはありません。可能な場合は、アンビエントオクルージョンを焼き込むことをお勧めします。
Height¶
マテリアルにDepthマップを設定すると、光線方向のサーチが行われ、ビュー方向に沿った凹凸の適切な変位がエミュレートされます。これは実際に追加されたジオメトリではなく、奥行きの錯覚です。複雑なオブジェクトでは機能しない場合がありますが、テクスチャにリアルな奥行き効果をもたらします。最良の結果を得るには、Depth を通常のマッピングと一緒に使用する必要があります。

サブサーフェススキャタリング¶
この効果は、オブジェクトの表面を透過し、散乱してから出る光をエミュレートします。リアルな肌、大理石、色のついた液体などを作成すると便利です。

Back Lighting¶
これは、明るい側(光源から見える)からの光が暗い側(光源とは反対側)に透過される量を制御します。これは、植物の葉、草、人間の耳などの薄いオブジェクトに適しています。
Refraction(屈折)¶
When refraction is enabled, Godot attempts to fetch information from behind the object being rendered. This allows distorting the transparency in a way similar to refraction in real life.
Remember to use a transparent albedo texture (or reduce the albedo color's alpha channel) to make refraction visible, as refraction relies on transparency to have a visible effect.
A normal map can optionally be specified in the Refraction Texture property to allow distorting the refraction's direction on a per-pixel basis.

注釈
Refraction is implemented as a screen-space effect and forces the material to be transparent. This makes the effect relatively fast, but this results in some limitations:
Transparency sorting issues may occur.
The refractive material cannot refract onto itself, or onto other transparent materials. A refractive material behind another transparent material will be invisible.
Off-screen objects cannot appear in the refraction. This is most noticeable with high refraction strength values.
Opaque materials in front of the refractive material will appear to have "refracted" edges, even though they shouldn't.
Detail(詳細)¶
Godot は、第二アルベドマップと法線マップを使用して、多くの方法でブレンドできるDetailテクスチャを生成することができます。これをセカンダリUV またはTriplanarモードと組み合わせることで、多くの興味深いテクスチャを実現できます。

ディテールの使用をコントロールする設定がいくつかあります。
Mask: The detail mask is a black and white image used to control where the blending takes place on a texture. White is for the detail textures, Black is for the regular material textures, different shades of gray are for partial blending of the material textures and detail textures.
Blend Mode: これらの4つのモードは、テクスチャのブレンド方法をコントロールします。
Mix: Combines pixel values of both textures. At black, only show the material texture, at white, only show the detail texture. Values of gray create a smooth blend between the two.
Add: Adds pixel values of one Texture with the other. Unlike mix mode both textures are completely mixed at white parts of a mask and not at gray parts. The original texture is mostly unchanged at black
Sub: Subtracts pixel values of one texture with the other. The second texture is completely subtracted at white parts of a mask with only a little subtraction in black parts, gray parts being different levels of subtraction based on the exact texture.
Mul: Multiplies the RGB channel numbers for each pixel from the top texture with the values for the corresponding pixel from the bottom texture.
Albedo: This is where you put an albedo texture you want to blend. If nothing is in this slot it will be interpreted as white by default.
Normal: This is where you put a normal texture you want to blend. If nothing is in this slot it will be interpreted as a flat normal map. This can still be used even if the material does not have normal map enabled.
UV1 and UV2(UV1およびUV2)¶
Godotは、マテリアルごとに2つのUVチャネルをサポートします。第二UVは、アンビエントオクルージョンまたは放出(焼き込みライト)に役立つことがよくあります。 UVはスケーリングとオフセットが可能で、繰り返しテクスチャを使用する場合に便利です。
Triplanar Mapping(三面マッピング)¶
Triplanarマッピングは、UV1とUV2の両方でサポートされています。これは、テクスチャ座標を取得する代替方法であり、「オートテクスチャ」とも呼ばれます。テクスチャは、X、Y、Zでサンプリングされ、法線によってブレンドされます。 Triplanarマッピングは、ワールド空間またはオブジェクト空間で実行できます。
下の画像では、すべてのプリミティブがワールドTriplanarと同じマテリアルを共有する方法を確認できるため、レンガのテクスチャはそれらの間でスムーズに連続しています。
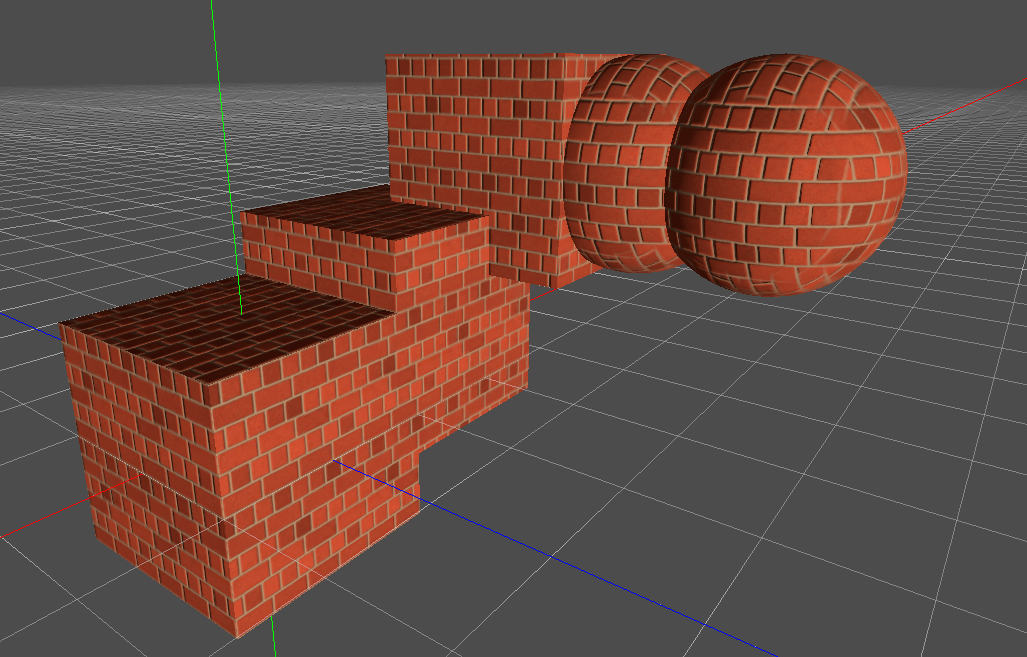
World Triplanar(ワールド空間でのTriplanar)¶
When using triplanar mapping, it is computed in object local space. This option makes it use world space instead.
Sampling¶
フィルター¶
The filtering method for the textures used by the material. See this page for a full list of options and their description.
繰り返し¶
if the textures used by the material repeat, and how they repeat. See this page for a full list of options and their description.
シャドウ¶
シャドウを受け取らない¶
オブジェクトに影を付けないようにします。
Use Shadow to Opacity(影を不透明度に使用)¶
ライティングはアルファを修正し、影のある領域は不透明になり、影のない領域は透明になります。 ARのカメラフィードに影を重ねるのに便利です。
Billboard¶
Billboard Mode(ビルボードモード)¶
描画するマテリアルのビルボード モードを有効にします。これは、オブジェクトがカメラに向く方法を制御します:
Disabled: ビルボードモードは無効です。
Enabled: Billboard mode is enabled. The object's -Z axis will always face the camera's viewing plane.
Y-Billboard: The object's X axis will always be aligned with the camera's viewing plane.
Particle Billboard: Most suited for particle systems, because it allows specifying flipbook animation.
The Particles Anim section is only visible when the billboard mode is Particle Billboard.
Billboard Keep Scale(ビルボードキープスケール)¶
ビルボードモードでメッシュのスケーリングを有効にします。
Grow(成長/拡張)¶
法線が指す方向にオブジェクトの頂点を成長させます:
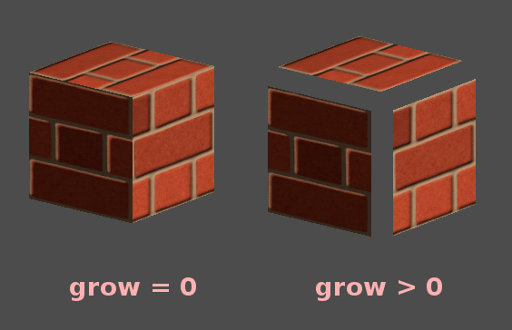
これは、一般的に安価にアウトラインを作成するために使用されます。2 番目のマテリアル パスを追加し、その色を黒にし、シェーディングなし、逆カリング(Cull Front)にして、Growをチックしたものをいくつか追加します:

トランスフォーム¶
Fixed Size(固定サイズ)¶
これにより、オブジェクトは距離に関係なく同じサイズでレンダリングされます。これは主にインジケーター(深度テストなし、高いレンダリング優先度)および一部のタイプのビルボードに役立ちます。
Use Point Size(ポイントのサイズを使用)¶
This option is only effective when the geometry rendered is made of points (generally it's made of triangles when imported from 3D modeling software). If so, then those points can be resized (see below).
Point Size(ポイントサイズ)¶
ポイントを描画するときの、ポイントサイズをピクセル単位で指定します。
Transmission¶
これは、明るい側(光源から見える)からの光が暗い側(光源とは反対側)に透過される量を制御します。これは、植物の葉、草、人間の耳などの薄いオブジェクトに適しています。

Proximity and Distance Fade¶
Godot allows materials to fade by proximity to each other as well as depending on the distance from the viewer. Proximity fade is useful for effects such as soft particles or a mass of water with a smooth blending to the shores.
Distance fade is useful for light shafts or indicators that are only present after a given distance.
Keep in mind enabling proximity fade or distance fade with Pixel Alpha mode enables alpha blending. Alpha blending is more GPU-intensive and can cause transparency sorting issues. Alpha blending also disables many material features such as the ability to cast shadows. To hide a character when they get too close to the camera, consider using Pixel Dither or better, Object Dither (which is even faster than Pixel Dither).
Material Settings¶
Render priority(レンダリングの優先度)¶
オブジェクトのレンダリング順序は変更できますが、これは主に透明なオブジェクト(または、床の亀裂などの深さの描画は行うが色の描画は行わない不透明なオブジェクト)に役立ちます。
Next Pass¶
Sets the material to be used for the next pass. This renders the object again with a different material.