Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
レイキャスティング¶
はじめに¶
ゲーム開発で最も一般的なタスクの1つは、レイ(またはカスタム形状のオブジェクト)をキャストし、そのヒットをチェックすることです。 これにより、複雑な動作、AIなどを実行できます。 このチュートリアルでは、2Dおよび3Dでこれを行う方法について説明します。
Godot stores all the low level game information in servers, while the scene is only a frontend. As such, ray casting is generally a lower-level task. For simple raycasts, nodes like RayCast3D and RayCast2D will work, as they return every frame what the result of a raycast is.
多くの場合、レイキャストはよりインタラクティブなプロセスである必要があるため、コードでこれを行う方法が必要です。
Space¶
In the physics world, Godot stores all the low level collision and physics information in a space. The current 2d space (for 2D Physics) can be obtained by accessing CanvasItem.get_world_2d().space. For 3D, it's Node3D.get_world_3d().space.
The resulting space RID can be used in PhysicsServer3D and PhysicsServer2D respectively for 3D and 2D.
spaceへのアクセス¶
Godot physics runs by default in the same thread as game logic, but may be set to run on a separate thread to work more efficiently. Due to this, the only time accessing space is safe is during the Node._physics_process() callback. Accessing it from outside this function may result in an error due to space being locked.
To perform queries into physics space, the PhysicsDirectSpaceState2D and PhysicsDirectSpaceState3D must be used.
2Dでは、次のコードを使用します:
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_rid = get_world_2d().space
var space_state = PhysicsServer2D.space_get_direct_state(space_rid)
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceRid = GetWorld2D().Space;
var spaceState = Physics2DServer.SpaceGetDirectState(spaceRid);
}
またはより直接的に:
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_2d().direct_space_state
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceState = GetWorld2D().DirectSpaceState;
}
そして、3Dで:
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_3d().direct_space_state
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceState = GetWorld3D().DirectSpaceState;
}
レイキャストクエリ¶
For performing a 2D raycast query, the method PhysicsDirectSpaceState2D.intersect_ray() may be used. For example:
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_2d().direct_space_state
# use global coordinates, not local to node
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.create(Vector2(0, 0), Vector2(50, 100))
var result = space_state.intersect_ray(query)
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceState = GetWorld2D().DirectSpaceState;
// use global coordinates, not local to node
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.Create(Vector2.Zero, new Vector2(50, 100));
var result = spaceState.IntersectRay(query);
}
結果はdictionaryです。 光線が何もヒットしなかった場合、dictionaryは空になります。 何かにヒットした場合、衝突情報が含まれます:
if result:
print("Hit at point: ", result.position)
if (result.Count > 0)
GD.Print("Hit at point: ", result["position"]);
衝突が発生した場合の result というdictionaryには、次のデータが含まれます:
{
position: Vector2 # point in world space for collision
normal: Vector2 # normal in world space for collision
collider: Object # Object collided or null (if unassociated)
collider_id: ObjectID # Object it collided against
rid: RID # RID it collided against
shape: int # shape index of collider
metadata: Variant() # metadata of collider
}
The data is similar in 3D space, using Vector3 coordinates. Note that to enable collisions
with Area3D, the boolean parameter collide_with_areas must be set to true.
const RAY_LENGTH = 1000
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_3d().direct_space_state
var cam = $Camera3D
var mousepos = get_viewport().get_mouse_position()
var origin = cam.project_ray_origin(mousepos)
var end = origin + cam.project_ray_normal(mousepos) * RAY_LENGTH
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters3D.create(origin, end)
query.collide_with_areas = true
var result = space_state.intersect_ray(query)
コリジョンの例外¶
レイキャスティングの一般的な使用例は、キャラクターが周囲の世界に関するデータを収集できるようにすることです。 これに関する1つの問題は、同じキャラクターにコライダーがあるため、次の画像に示すように、レイは親のコライダーのみを検出することです:

To avoid self-intersection, the intersect_ray() parameters object can take an
array of exceptions via its exclude property. This is an example of how to use it
from a CharacterBody2D or any other collision object node:
extends CharacterBody2D
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_2d().direct_space_state
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.create(global_position, player_position)
query.exclude = [self]
var result = space_state.intersect_ray(query)
using Godot;
public partial class MyCharacterBody2D : CharacterBody2D
{
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceState = GetWorld2D().DirectSpaceState;
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.Create(globalPosition, playerPosition);
query.Exclude = new Godot.Collections.Array<Rid> { GetRid() };
var result = spaceState.IntersectRay(query);
}
}
例外配列には、オブジェクトまたは RID を含めることができます。
コリジョンマスク¶
例外メソッドは親ボディを除外するためにうまく機能しますが、例外の大きなリストや動的リストが必要な場合は非常に不便になります。 この場合、コリジョンレイヤー/マスクシステムを使用する方がはるかに効率的です。
The intersect_ray() parameters object can also be supplied a collision mask.
For example, to use the same mask as the parent body, use the collision_mask
member variable. The array of exceptions can be supplied as the last argument as well:
extends CharacterBody2D
func _physics_process(delta):
var space_state = get_world_2d().direct_space_state
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.create(global_position, target_position,
collision_mask, [self])
var result = space_state.intersect_ray(query)
using Godot;
public partial class MyCharacterBody2D : CharacterBody2D
{
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
var spaceState = GetWorld2D().DirectSpaceState;
var query = PhysicsRayQueryParameters2D.Create(globalPosition, targetPosition,
CollisionMask, new Godot.Collections.Array<Rid> { GetRid() });
var result = spaceState.IntersectRay(query);
}
}
See Code example for details on how to set the collision mask.
画面からの3Dレイキャスティング¶
Casting a ray from screen to 3D physics space is useful for object picking. There is not much need to do this because CollisionObject3D has an "input_event" signal that will let you know when it was clicked, but in case there is any desire to do it manually, here's how.
To cast a ray from the screen, you need a Camera3D
node. A Camera3D can be in two projection modes: perspective and
orthogonal. Because of this, both the ray origin and direction must be
obtained. This is because origin changes in orthogonal mode, while
normal changes in perspective mode:
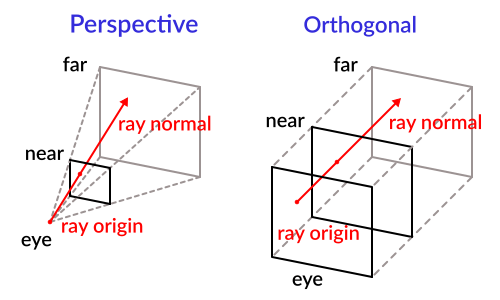
カメラを使用して取得するには、次のコードを使用できます:
const RAY_LENGTH = 1000.0
func _input(event):
if event is InputEventMouseButton and event.pressed and event.button_index == 1:
var camera3d = $Camera3D
var from = camera3d.project_ray_origin(event.position)
var to = from + camera3d.project_ray_normal(event.position) * RAY_LENGTH
private const float RayLength = 1000.0f;
public override void _Input(InputEvent @event)
{
if (@event is InputEventMouseButton eventMouseButton && eventMouseButton.Pressed && eventMouseButton.ButtonIndex == MouseButton.Left)
{
var camera3D = GetNode<Camera3D>("Camera3D");
var from = camera3D.ProjectRayOrigin(eventMouseButton.Position);
var to = from + camera3D.ProjectRayNormal(eventMouseButton.Position) * RayLength;
}
}
_input() 中はspaceがロックされる可能性があるため、実際にはこのクエリは _physics_process() で実行する必要があることに注意してください。