Work in progress
The content of this page was not yet updated for Godot
4.2
and may be outdated. If you know how to improve this page or you can confirm
that it's up to date, feel free to open a pull request.
Prototipando niveles con CSG¶
CSG stands for Constructive Solid Geometry, and is a tool to combine basic shapes or custom meshes to create more complex shapes. In 3D modeling software, CSG is mostly known as "Boolean Operators".
Level prototyping is one of the main uses of CSG in Godot. This technique allows users to create the most common shapes by combining primitives. Interior environments can be created by using inverted primitives.
Nota
The CSG nodes in Godot are mainly intended for prototyping. There is no built-in support for UV mapping or editing 3D polygons (though extruded 2D polygons can be used with the CSGPolygon3D node).
If you're looking for an easy to use level design tool for a project, you may want to use Qodot instead. It lets you design levels using TrenchBroom and import them in Godot.
Ver también
You can check how to use CSG nodes to build various shapes (such as stairs or roads) using the Constructive Solid Geometry demo project.
Introducción a nodos CSG¶
Al igual que otras características de Godot, el CSG se apoya en forma de nodos. Estos son los nodos de CSG:
CSGCylinder3D (also supports cone)

Funcionalidades de herramientas CSG¶
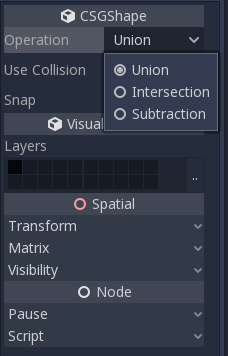
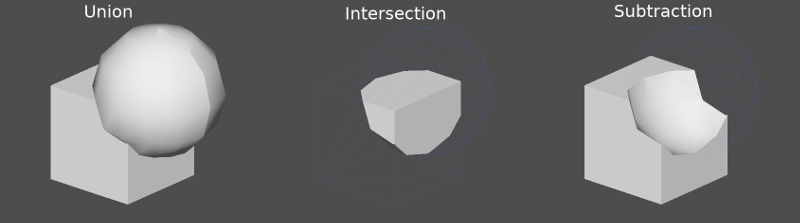
Cada nodo CSG soporta 3 tipos de operaciones booleanas:
Unión: La geometría de ambas primitivas se fusiona, la geometría que se intersecta se elimina.
Intersección: Sólo queda la geometría de intersección, el resto se elimina.
Sustracción: La segunda forma se resta de la primera, dejando una mella con su forma.
PolígonoCSG¶
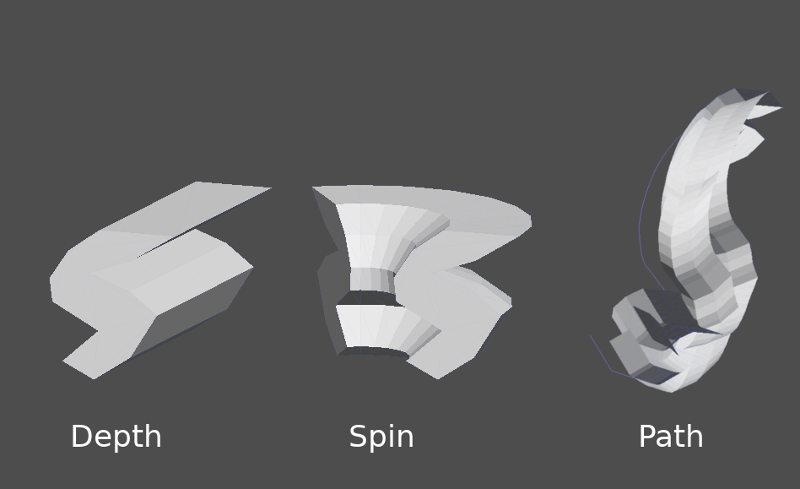
The CSGPolygon3D node extrude along a Polygon drawn in 2D (in X, Y coordinates) in the following ways:
Profundidad: Extraído de vuelta una cantidad dada.
Girar: Extruido mientras gira alrededor de su origen.
Ruta: Extruido a lo largo de un nodo Ruta. Esta operación se llama comúnmente "lofting".
Nota
The Path mode must be provided with a Path3D node to work. In the Path node, draw the path and the polygon in CSGPolygon3D will extrude along the given path.
Mallas personalizadas¶
Any mesh can be used for CSGMesh3D; the mesh can be modeled in other software and imported into Godot. Multiple materials are supported. There are some restrictions for geometry:
debe ser cerrada,
no debe intersectarse a si mismo,
no debe contener caras internas,
cada borde debe conectarse sólo a otras dos caras.
CSGCombiner3D¶
The CSGCombiner3D node is an empty shape used for organization. It will only combine children nodes.
Orden de procesamiento¶
Every CSG node will first process its children nodes and their operations: union, intersection, or subtraction, in tree order, and apply them to itself one after the other.
Nota
En interés del rendimiento, asegúrese de que la geometría del CSG siga siendo relativamente simple, ya que las mallas complejas pueden tardar un tiempo en procesarse. Si se agregan objetos juntos (como objetos de mesa y de habitación), crearlos como árboles CSG separados. Forzar demasiados objetos en un solo árbol eventualmente comenzará a afectar el rendimiento. Utiliza las operaciones binarias sólo donde realmente las necesites.
Prototipando un nivel¶
Haremos un prototipo de una sala para practicar el uso de herramientas CSG.
Truco
Trabajar en la proyección Ortonormal da una mejor visión al combinar las formas del CSG.
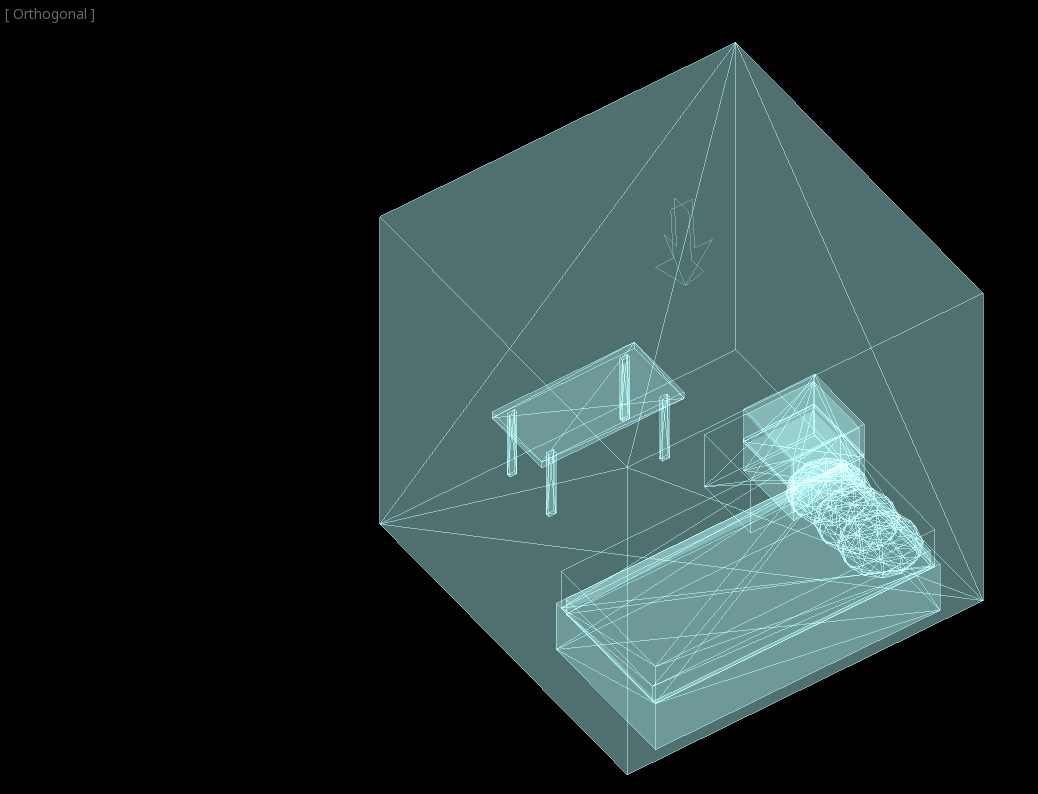
Nuestro nivel contendrá estos objetos:
una habitación,
una cama,
una lámpara,
un escritorio,
una estantería.
Create a scene with a Node3D node as root node.
Truco
La iluminación por defecto del entorno no proporciona un sombreado claro en algunos ángulos. Cambia el modo de visualización usando Display Overdraw en el menú de vista 3D, o añade un nodo DirectionalLight para ayudarte a ver con claridad.
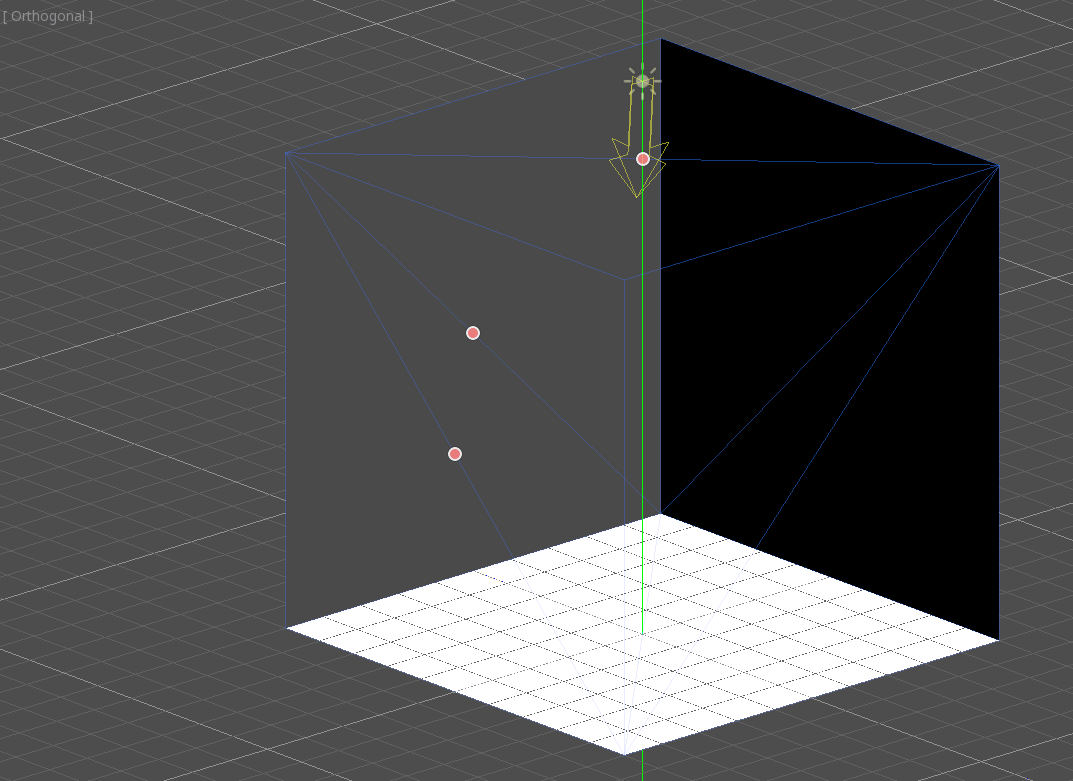
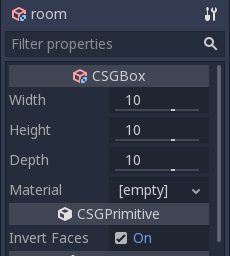
Create a CSGBox3D and name it room, enable Invert Faces and change the
dimensions of your room.
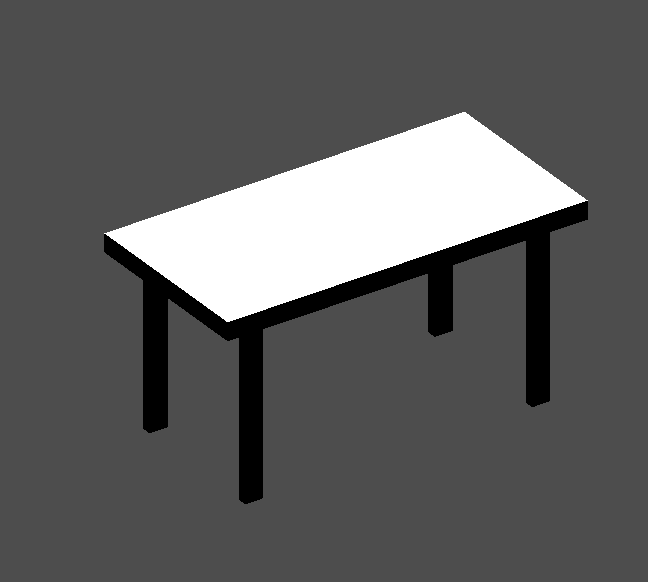
Next, create a CSGCombiner3D and name it desk.
Un escritorio tiene una superficie y 4 patas:
Create 1 CSGBox3D children node in Union mode for the surface and adjust the dimensions.
Create 4 CSGBox3D children nodes in Union mode for the legs and adjust the dimensions.
Ajusta su ubicación para que se parece a un escritorio.
Nota
CSG nodes inside a CSGCombiner3D will only process their operation within the combiner. Therefore, CSGCombiner3Ds are used to organize CSG nodes.
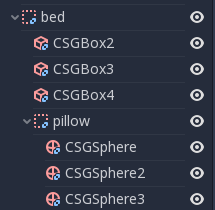
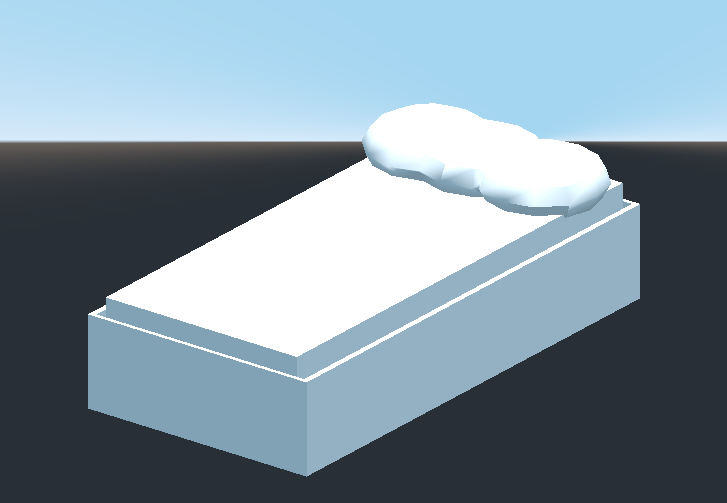
Create a CSGCombiner3D and name it bed.
Our bed consists of 3 parts: the bed, the mattress and a pillow. Create a CSGBox3D and adjust its dimension for the bed. Create another CSGBox3D and adjust its dimension for the mattress.

We will create another CSGCombiner3D named pillow as the child of bed.
The scene tree should look like this:
We will combine 3 CSGSphere3D nodes in Union mode to form a pillow. Scale the Y axis of the spheres and enable Smooth Faces.
Selecciona el nodo pillow y cambia el modo a Sustracción; las esferas combinadas harán un agujero en el colchón.
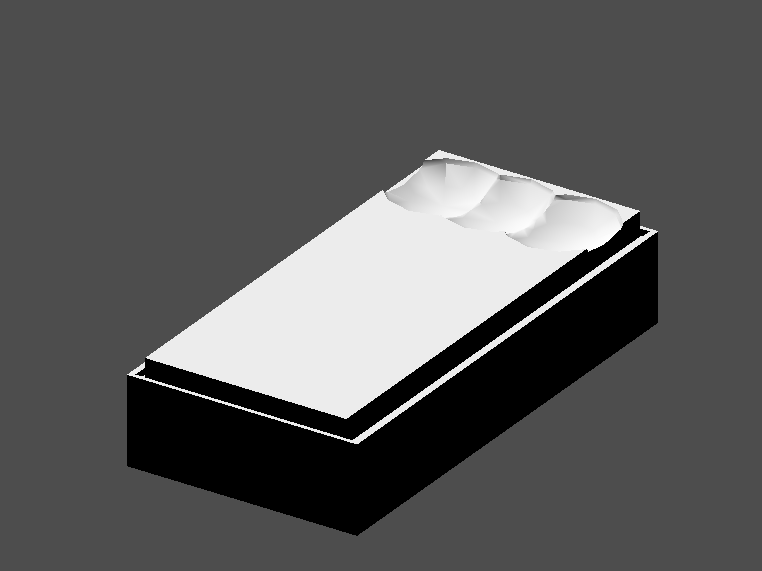

Try to re-parent the pillow node to the root Node3D node; the hole will
disappear.
Nota
This is to illustrate the effect of CSG processing order. Since the root node is not a CSG node, the CSGCombiner3D nodes are the end of the operations; this shows the use of CSGCombiner3D to organize the CSG scene.
Deshacer el parentesco después de observar el efecto. La cama que has construido debería ser así:
Create a CSGCombiner3D and name it lamp.
A lamp consists of 3 parts: the stand, the pole and the lampshade. Create a CSGCylinder3D, enable the Cone option and make it the stand. Create another CSGCylinder3D and adjust the dimensions to use it as a pole.
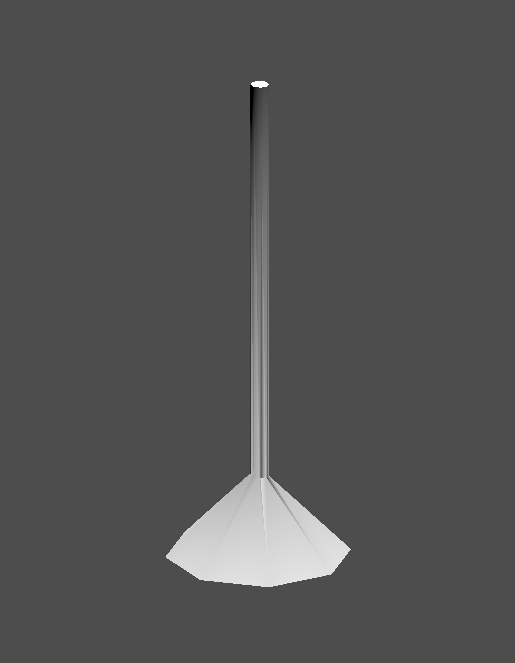

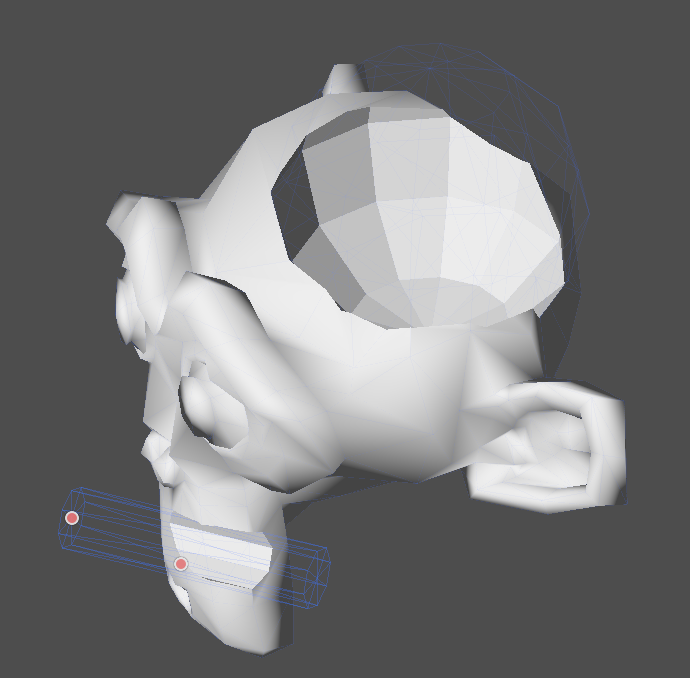
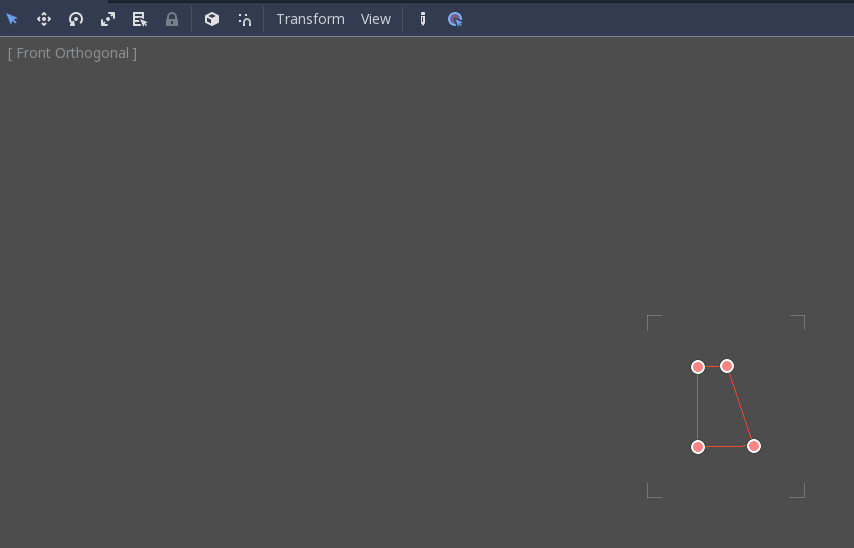
We will use a CSGPolygon3D for the lampshade. Use the Spin mode for the CSGPolygon3D and draw a trapezoid while in Front View (numeric keypad 1); this shape will extrude around the origin and form the lampshade.
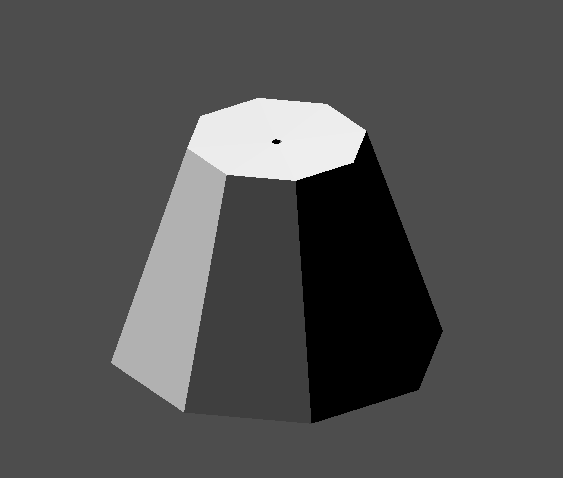

Ajusta la colocación de las 3 partes para que parezca una lámpara.

Create a CSGCombiner3D and name it bookshelf.
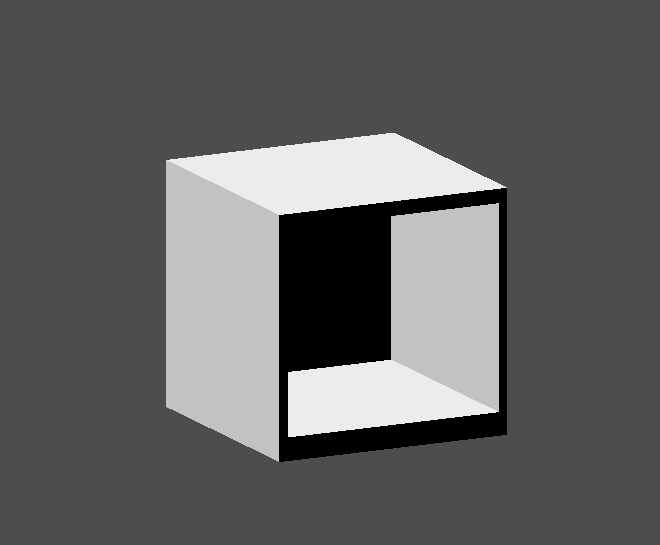
We will use 3 CSGBox3D nodes for the bookshelf. Create a CSGBox3D and adjust its dimensions; this will be the size of the bookshelf.
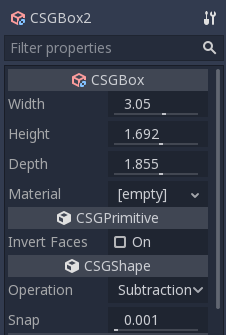
Duplicate the CSGBox3D and shorten the dimensions of each axis and change the mode to Subtraction.
You've almost built a shelf. Create one more CSGBox3D for dividing the shelf into two levels.
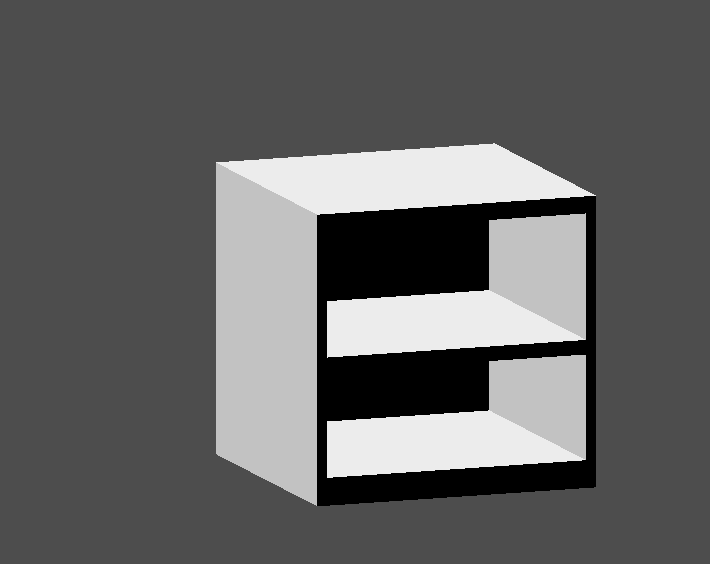
Ubica los muebles en el cuarto del modo que desees, tu escene debería verse así:
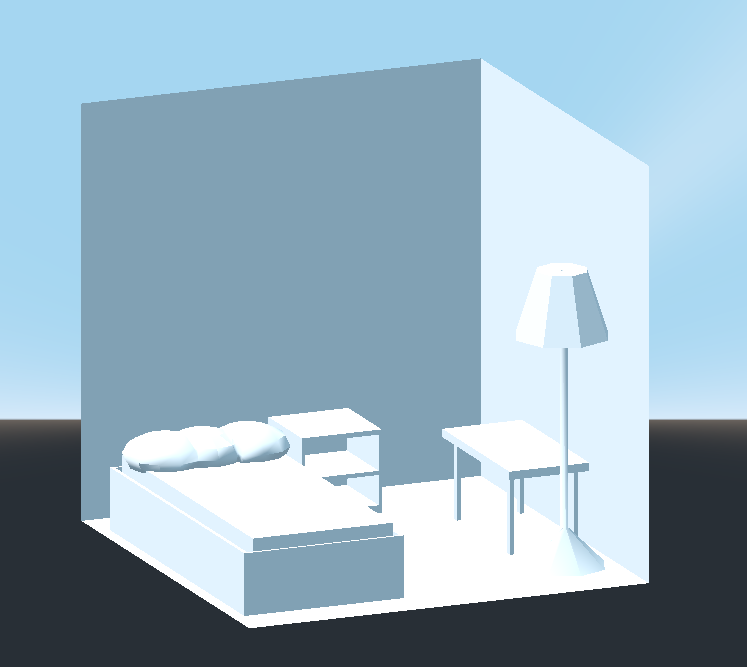

Has hecho un prototipo con éxito de una habitación con las herramientas CSG en Godot. Las herramientas CSG pueden utilizarse para diseñar todo tipo de niveles, como un laberinto o una ciudad; explora sus limitaciones a la hora de diseñar tu juego.
Usando texturas prototipo¶
Godot's Standard Material 3D and ORM Material 3D supports triplanar mapping, which can be used to automatically apply a texture to arbitrary objects without distortion. This is handy when using CSG as Godot doesn't support editing UV maps on CSG nodes yet. Triplanar mapping is relatively slow, which usually restricts its usage to organic surfaces like terrain. Still, when prototyping, it can be used to quickly apply textures to CSG-based levels.
Nota
Si necesitas algunas texturas para el prototipo, Kenney hizo unas "texturas de prototipo con licencia CC0" <https://kenney.nl/assets/prototype-textures>`__.
Existen dos modos de aplicar un material a un nodo CSG:
Applying it to a CSGCombiner3D node as a material override (Geometry > Material Override in the Inspector). This will affect its children automatically, but will make it impossible to change the material in individual children.
Aplicando un material a los nodos individuales (Material en el Inspector). De esta manera, cada nodo CSG puede tener su propia apariencia. Los nodos CSG sustractivos aplicarán su material a los nodos en los que están "excavando".
To apply triplanar mapping to a CSG node, select it, go to the Inspector, click the [empty] text next to Material Override (or Material for individual CSG nodes). Choose New StandardMaterial3D. Click the newly created material's icon to edit it. Unfold the Albedo section and load a texture into the Texture property. Now, unfold the Uv1 section and check Triplanar. You can change the texture offset and scale on each axis by playing with the Scale and Offset properties just above. Higher values in the Scale property will cause the texture to repeat more often.
Truco
You can copy a StandardMaterial3D to reuse it across CSG nodes. To do so, click the dropdown arrow next to a material property in the Inspector and choose Copy. To paste it, select the node you'd like to apply the material onto, click the dropdown arrow next to its material property then choose Paste.
Exporting as glTF¶
It can be useful to block out a level using CSG, then export it as a 3d model, to import into 3D modeling software. You can do this by selecting Scene > Export As... > glTF 2.0 Scene.