Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Compiling for Linux, *BSD¶
Ver también
Esta página describe cómo compilar los binarios del editor y las plantillas de exportación para Linux desde el código fuente. Si lo que buscas es exportar tu proyecto a Linux, consulta Exportando para Linux.
Requerimientos¶
Para compilar en Linux u otras variantes de Unix, se requiere lo siguiente:
GCC 7+ o Clang 6+.
El sistema de construcción SCons 3.0+.
Nota
If your distribution uses Python 2 by default, or you are using a version of SCons prior to 3.1.2, you will need to change the version of Python that SCons uses by changing the shebang (the first line) of the SCons script file to
#! /usr/bin/python3. Use the commandwhich sconsto find the location of the SCons script file.pkg-config (used to detect the development libraries listed below).
Librerías de desarrollo:
X11, Xcursor, Xinerama, Xi and XRandR.
MesaGL.
ALSA.
PulseAudio.
Opcional - libudev (compilar con
udev=yes).
Ver también
Para obtener el código fuente de Godot para compilarlo, consulta la sección Consiguiendo el código fuente.
Para obtener una visión general del uso de SCons para Godot, consulta la sección Introducción al sistema de compilación.
Líneas de comandos específicas para cada distribución¶
apk add \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
g++ \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev \
mesa-dev \
libexecinfo-dev \
eudev-dev \
alsa-lib-dev \
pulseaudio-dev
pacman -S --needed \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
libxcursor \
libxinerama \
libxi \
libxrandr \
mesa \
glu \
libglvnd \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
apt-get install \
build-essential \
scons \
pkg-config \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libgl1-mesa-dev \
libglu-dev \
libasound2-dev \
libpulse-dev \
libudev-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev
dnf install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
mesa-libGL-devel \
mesa-libGLU-devel \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-libs-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libstdc++-static \
libatomic-static
pkg install \
py37-scons \
pkgconf \
xorg-libraries \
libXcursor \
libXrandr \
libXi \
xorgproto libGLU \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
emerge -an \
dev-util/scons \
x11-libs/libX11 \
x11-libs/libXcursor \
x11-libs/libXinerama \
x11-libs/libXi \
media-libs/mesa \
media-libs/glu \
media-libs/alsa-lib \
media-sound/pulseaudio
urpmi \
scons \
task-c++-devel \
pkgconfig \
"pkgconfig(alsa)" \
"pkgconfig(glu)" \
"pkgconfig(libpulse)" \
"pkgconfig(udev)" \
"pkgconfig(x11)" \
"pkgconfig(xcursor)" \
"pkgconfig(xinerama)" \
"pkgconfig(xi)" \
"pkgconfig(xrandr)"
pkg_add \
python \
scons \
llvm
zypper install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
Mesa-libGL-devel \
alsa-devel \
libpulse-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libGLU1
pkg_add \
pkg-config \
py37-scons
Consejo
Para tener soporte de audio, opcionalmente puedes instalar "pulseaudio".
eopkg install -c \
system.devel \
scons \
libxcursor-devel \
libxinerama-devel \
libxi-devel \
libxrandr-devel \
mesalib-devel \
libglu \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-devel
Compilando¶
Inicia una terminal, ve al directorio raíz del código fuente del motor y escribe:
scons platform=linuxbsd
Nota
Prior to Godot 4.0, the Linux/*BSD target was called x11 instead of
linuxbsd. If you are looking to compile Godot 3.x, make sure to use the
3.x branch of this documentation.
If all goes well, the resulting binary executable will be placed in the "bin" subdirectory. This executable file contains the whole engine and runs without any dependencies. Executing it will bring up the Project Manager.
Nota
Si deseas compilar utilizando Clang en lugar de GCC, usa este comando:
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes
El uso de Clang parece ser un requisito para OpenBSD, de lo contrario, las fuentes no se compilarían correctamente.
Nota
If you are compiling Godot for production use, then you can
make the final executable smaller and faster by adding the
SCons options target=template_release production=yes.
If you are compiling Godot with GCC, you can make the binary
even smaller and faster by adding the SCons option lto=full.
As link-time optimization is a memory-intensive process,
this will require about 7 GB of available RAM while compiling.
Nota
Si deseas utilizar configuraciones de editor separadas para tus propias compilaciones de Godot y las versiones oficiales, puedes habilitar Modo autónomo creando un archivo llamado ._sc_ o _sc_ en la carpeta bin/.
Running a headless/server build¶
To run in headless mode which provides editor functionality to export projects in an automated manner, use the normal build:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=editor
And then use the --headless command line argument:
./bin/godot.linuxbsd.editor.x86_64 --headless
Para compilar una versión servidor con depuración que se puede utilizar con herramientas de depuración remota, utiliza:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug
Para compilar una versión servidor que está optimizada para ejecutar servidores de juegos dedicados, utiliza:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release production=yes
Construyendo plantillas de exportación¶
Advertencia
Las binarias de Linux generalmente no se ejecutarán en distribuciones más antiguas que la distribución en la que fueron compiladas. Si deseas distribuir binarios que funcionen en la mayoría de las distribuciones, debes compilarlos en una distribución antigua como Ubuntu 16.04. Puedes utilizar una máquina virtual o un contenedor para configurar un entorno de compilación adecuado.
To build Linux or *BSD export templates, run the build system with the following parameters:
(32 bits)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_32
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_32
(64 bits)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_64
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_64
Ten en cuenta que la compilación cruzada para bits opuestos (64/32) a los de tu plataforma de host no siempre es sencilla y puede requerir un entorno chroot.
To create standard export templates, the resulting files in the bin/ folder
must be copied to:
$HOME/.local/share/godot/export_templates/<version>/
and named like this (even for *BSD which is seen as "Linux/X11" by Godot):
linux_x11_32_debug
linux_x11_32_release
linux_x11_64_debug
linux_x11_64_release
Sin embargo, si estás escribiendo tus propios módulos personalizados o código C++ personalizado, es posible que desees configurar tus binarios como plantillas de exportación personalizadas aquí:
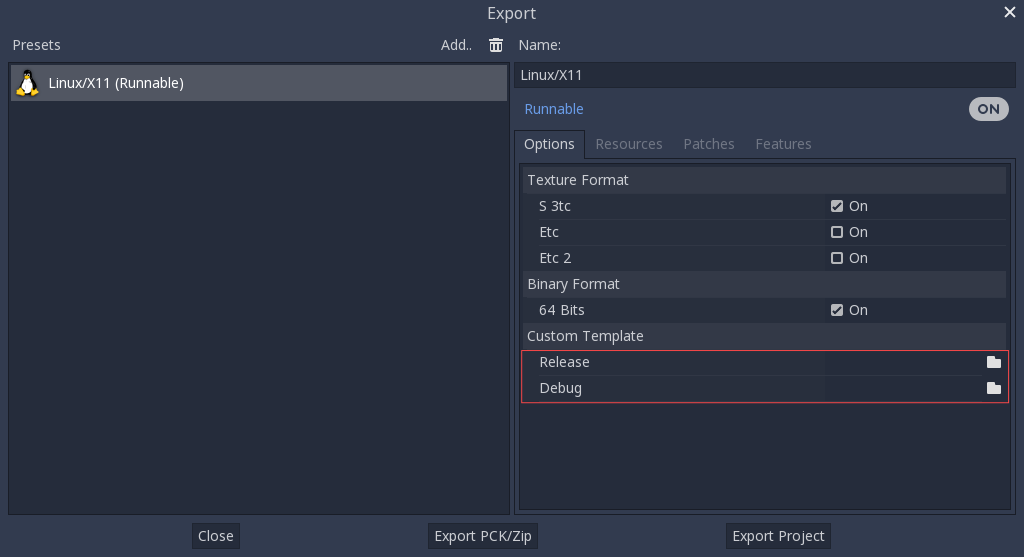
Ni siquiera necesitas copiarlos, simplemente puedes hacer referencia a los archivos resultantes en el directorio bin/ de la carpeta de origen de Godot, de esta manera, la próxima vez que construyas, automáticamente tendrás las plantillas personalizadas referenciadas.
Utilizando Clang y LLD para un desarrollo más rápido¶
También puedes usar Clang y LLD para compilar Godot. Esto tiene dos ventajas en comparación con la configuración predeterminada de GCC + GNU ld:
LLD enlaza Godot significativamente más rápido en comparación con GNU ld o gold. Esto lleva a tiempos de iteración más rápidos.
Clang tiende a proporcionar mensajes de error más útiles en comparación con GCC.
Para hacerlo, instala Clang y el paquete lld desde el administrador de paquetes de tu distribución y luego utiliza el siguiente comando de SCons:
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes linker=lld
Después de que se complete la compilación, se creará un nuevo archivo binario con el sufijo .llvm en la carpeta bin/.
Todavía se recomienda usar GCC para las compilaciones de producción, ya que se pueden compilar utilizando la optimización en tiempo de enlace, lo que hace que los archivos binarios resultantes sean más pequeños y rápidos.
If this error occurs:
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l:libatomic.a: No such file or directory
There are two solutions:
In your SCons command, add the parameter
use_static_cpp=no.Follow these instructions to configure, build, and install
libatomic_ops. Then, copy/usr/lib/libatomic_ops.ato/usr/lib/libatomic.a, or create a soft link tolibatomic_opsby commandln -s /usr/lib/libatomic_ops.a /usr/lib/libatomic.a. The soft link can ensure the latestlibatomic_opswill be used without the need to copy it everytime when it is updated.
Using mold for faster development¶
For even faster linking compared to LLD, you can use mold. mold can be used with either GCC or Clang.
As of January 2023, mold is not readily available in Linux distribution repositories, so you will have to install its binaries manually.
Descarga binarios de mold desde su página de lanzamientos.
Extract the
.tar.gzfile, then move the extraced folder to a location such as.local/share/mold.Add
$HOME/.local/share/mold/binto your user'sPATHenvironment variable. For example, you can add the following line at the end of your$HOME/.bash_profilefile:
PATH="$HOME/.local/share/mold/bin:$PATH"
Open a new terminal (or run
source "$HOME/.bash_profile"), then use the following SCons command when compiling Godot:scons platform=linuxbsd linker=mold
Using system libraries for faster development¶
Godot bundles the source code of various third-party libraries. You can choose to use system versions of third-party libraries instead. This makes the Godot binary faster to link, as third-party libraries are dynamically linked. Therefore, they don't need to be statically linked every time you build the engine (even on small incremental changes).
However, not all Linux distributions have packages for third-party libraries available (or they may not be up-to-date).
Moving to system libraries can reduce linking times by several seconds on slow CPUs, but it requires manual testing depending on your Linux distribution. Also, you may not be able to use system libraries for everything due to bugs in the system library packages (or in the build system, as this feature is less tested).
To compile Godot with system libraries, install these dependencies on top of the ones listed in the Líneas de comandos específicas para cada distribución:
Fedora |
sudo dnf install embree3-devel enet-devel glslang-devel graphite2-devel harfbuzz-devel libicu-devel \
libsquish-devel libtheora-devel libvorbis-devel libwebp-devel libzstd-devel mbedtls-devel \
miniupnpc-devel
|
After installing all required packages, use the following command to build Godot:
scons platform=linuxbsd builtin_embree=no builtin_enet=no builtin_freetype=no builtin_graphite=no builtin_harfbuzz=no builtin_libogg=no builtin_libpng=no builtin_libtheora=no builtin_libvorbis=no builtin_libwebp=no builtin_mbedtls=no builtin_miniupnpc=no builtin_pcre2=no builtin_zlib=no builtin_zstd=no
You can view a list of all built-in libraries that have system alternatives by
running scons -h, then looking for options starting with builtin_.
Advertencia
When using system libraries, the resulting library is not portable across Linux distributions anymore. Do not use this approach for creating binaries you intend to distribute to others, unless you're creating a package for a Linux distribution.
Usando Pyston para un desarrollo mas rápido¶
Puedes usar Pyston para ejecutar SCons. Pyston es una implementación habilitada para JIT (Just-In-Time) del lenguaje Python (en el que está escrito SCons). Actualmente solo es compatible con Linux. Pyston puede acelerar significativamente las compilaciones incrementales, a menudo en un factor entre 1.5× y 2×. Pyston se puede combinar con Clang y LLD para obtener compilaciones aún más rápidas.
Descarga la última versión portátil de Pyston.
Extrae el archivo portátil
.tar.gzen una ubicación específica, como por ejemplo$HOME/.local/opt/pyston/(crea las carpetas si es necesario).Utiliza
cdpara acceder a la carpeta extraída de Pyston desde una terminal, luego ejecuta./pyston -m pip install sconspara instalar SCons dentro de Pyston.Para facilitar la ejecución de SCons a través de Pyston, crea un enlace simbólico del script de envoltura en una ubicación de tu variable de entorno
PATH:ln -s ~/.local/opt/pyston/bin/scons ~/.local/bin/pyston-scons
En lugar de ejecutar
scons <argumentos de compilación>, ejecutapyston-scons <argumentos de compilación>para compilar Godot.
Si no puedes ejecutar pyston-scons después de crear el enlace simbólico, asegúrate de que $HOME/.local/bin/ forme parte de la variable de entorno PATH de tu usuario.
Nota
Alternatively, you can run python -m pip install pyston_lite_autoload
then run SCons as usual. This will automatically load a subset of Pyston's
optimizations in any Python program you run. However, this won't bring as
much of a performance improvement compared to installing "full" Pyston.