Up to date
This page is up to date for Godot 4.2.
If you still find outdated information, please open an issue.
Compiling for Linux, *BSD¶
Voir aussi
Cette page décrit comment compiler l'éditeur Linux et les modèles d'exportation depuis le code source. Si vous cherchez à exporter votre projet pour Linux, référez-vous à Exportation pour Linux.
Pré-requis¶
Pour la compilation sous Linux ou d'autres variantes Unix, les éléments suivants sont requis :
GCC 7+ ou Clang 6+.
SCons 3.0+ système de construction(build).
Note
If your distribution uses Python 2 by default, or you are using a version of SCons prior to 3.1.2, you will need to change the version of Python that SCons uses by changing the shebang (the first line) of the SCons script file to
#! /usr/bin/python3. Use the commandwhich sconsto find the location of the SCons script file.pkg-config (used to detect the development libraries listed below).
Development libraries:
X11, Xcursor, Xinerama, Xi and XRandR.
MesaGL.
ALSA.
PulseAudio.
Facultatif - libudev (construit(build) avec
udev=yes).
Voir aussi
Pour récupérer le code source de Godot pour le compiler, voir Obtenir la source.
Pour un aperçu général de l'utilisation de SCons pour Godot, voir Introduction au buildsystem.
Lignes uniques spécifiques à la distribution¶
apk add \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
g++ \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev \
mesa-dev \
libexecinfo-dev \
eudev-dev \
alsa-lib-dev \
pulseaudio-dev
pacman -S --needed \
scons \
pkgconf \
gcc \
libxcursor \
libxinerama \
libxi \
libxrandr \
mesa \
glu \
libglvnd \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
apt-get install \
build-essential \
scons \
pkg-config \
libx11-dev \
libxcursor-dev \
libxinerama-dev \
libgl1-mesa-dev \
libglu-dev \
libasound2-dev \
libpulse-dev \
libudev-dev \
libxi-dev \
libxrandr-dev
dnf install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
mesa-libGL-devel \
mesa-libGLU-devel \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-libs-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libstdc++-static \
libatomic-static
pkg install \
py37-scons \
pkgconf \
xorg-libraries \
libXcursor \
libXrandr \
libXi \
xorgproto libGLU \
alsa-lib \
pulseaudio
emerge -an \
dev-util/scons \
x11-libs/libX11 \
x11-libs/libXcursor \
x11-libs/libXinerama \
x11-libs/libXi \
media-libs/mesa \
media-libs/glu \
media-libs/alsa-lib \
media-sound/pulseaudio
urpmi \
scons \
task-c++-devel \
pkgconfig \
"pkgconfig(alsa)" \
"pkgconfig(glu)" \
"pkgconfig(libpulse)" \
"pkgconfig(udev)" \
"pkgconfig(x11)" \
"pkgconfig(xcursor)" \
"pkgconfig(xinerama)" \
"pkgconfig(xi)" \
"pkgconfig(xrandr)"
pkg_add \
python \
scons \
llvm
zypper install \
scons \
pkgconfig \
libX11-devel \
libXcursor-devel \
libXrandr-devel \
libXinerama-devel \
libXi-devel \
Mesa-libGL-devel \
alsa-devel \
libpulse-devel \
libudev-devel \
gcc-c++ \
libGLU1
pkg_add \
pkg-config \
py37-scons
Indication
Pour le support audio, vous pouvez optionnellement installer pulseaudio.
eopkg install -c \
system.devel \
scons \
libxcursor-devel \
libxinerama-devel \
libxi-devel \
libxrandr-devel \
mesalib-devel \
libglu \
alsa-lib-devel \
pulseaudio-devel
Compilation¶
Démarrez un terminal, allez à la racine du code source du moteur et tapez :
scons platform=linuxbsd
Note
Prior to Godot 4.0, the Linux/*BSD target was called x11 instead of
linuxbsd. If you are looking to compile Godot 3.x, make sure to use the
3.x branch of this documentation.
If all goes well, the resulting binary executable will be placed in the "bin" subdirectory. This executable file contains the whole engine and runs without any dependencies. Executing it will bring up the Project Manager.
Note
Si vous souhaitez compiler en utilisant Clang plutôt que GCC, utilisez cette commande :
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes
L'utilisation de Clang semble être une exigence pour OpenBSD, sinon les polices de caractères ne seraient pas construites(build).
Note
If you are compiling Godot for production use, then you can
make the final executable smaller and faster by adding the
SCons options target=template_release production=yes.
If you are compiling Godot with GCC, you can make the binary
even smaller and faster by adding the SCons option lto=full.
As link-time optimization is a memory-intensive process,
this will require about 7 GB of available RAM while compiling.
Note
Si vous souhaitez utiliser des paramètres d'édition séparés pour vos propres constructions Godot et vos versions officielles, vous pouvez activer Mode autonome en créant un fichier appelé ._sc_ ou _sc_ dans le dossier bin/.
Running a headless/server build¶
To run in headless mode which provides editor functionality to export projects in an automated manner, use the normal build:
scons platform=linuxbsd target=editor
And then use the --headless command line argument:
./bin/godot.linuxbsd.editor.x86_64 --headless
Pour compiler un build de débogage serveur qui peut être utilisé avec les outils de débogage à distance, utilisez : :
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug
Pour compiler un build serveur qui est optimisé pour faire fonctionner des serveurs de jeu dédiés, utilisez :
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release production=yes
Création de modèles d'exportation¶
Avertissement
Les binaires Linux ne fonctionnent généralement pas sur des distributions plus anciennes que celle sur laquelle ils ont été construits(build). Si vous souhaitez distribuer des binaires qui fonctionnent sur la plupart des distributions, vous devez les construire(build) sur une ancienne distribution telle que Ubuntu 16.04. Vous pouvez utiliser une machine virtuelle ou un conteneur pour mettre en place un environnement de compilation approprié.
To build Linux or *BSD export templates, run the build system with the following parameters:
(32 bits)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_32
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_32
(64 bits)
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_release arch=x86_64
scons platform=linuxbsd target=template_debug arch=x86_64
Notez que la compilation croisée pour les bits opposés (64/32) à votre plate-forme hôte n'est pas toujours simple et peut nécessiter un environnement chroot.
To create standard export templates, the resulting files in the bin/ folder
must be copied to:
$HOME/.local/share/godot/export_templates/<version>/
and named like this (even for *BSD which is seen as "Linux/X11" by Godot):
linux_x11_32_debug
linux_x11_32_release
linux_x11_64_debug
linux_x11_64_release
Cependant, si vous écrivez vos modules personnalisés ou du code C++ personnalisé, vous pouvez plutôt configurer vos binaires comme modèles d'exportation personnalisés ici :
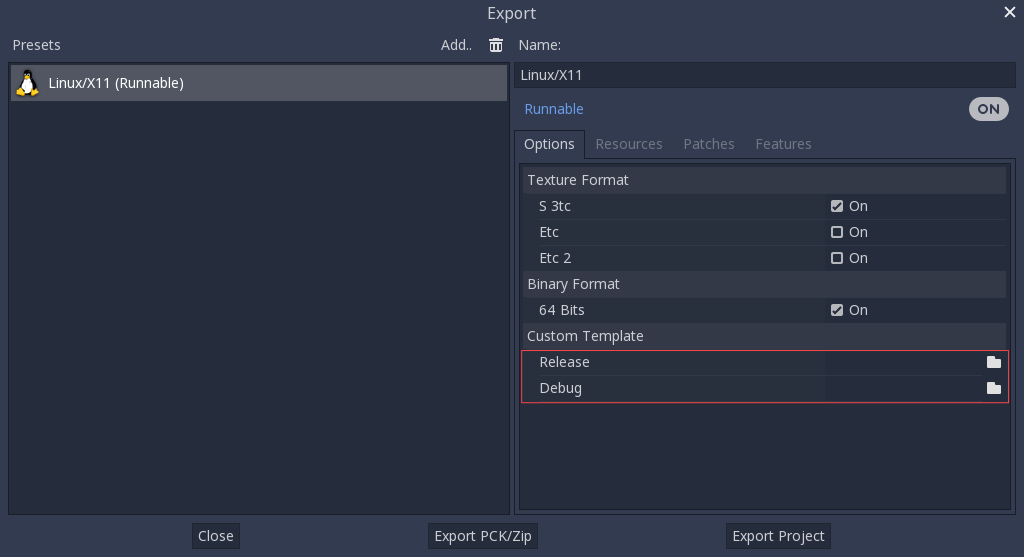
Vous n'avez même pas besoin de les copier, vous pouvez simplement référencer les fichiers résultants dans le répertoire bin/ de votre dossier source Godot, de sorte que la prochaine fois que vous construirez(build), vous aurez automatiquement les modèles personnalisés référencés.
Utiliser Clang et LLD pour un développement plus rapide¶
Vous pouvez également utiliser Clang et LLD pour construire(build) Godot. Cela présente deux avantages par rapport à la configuration par défaut de GCC + GNU ld :
LLD relie(links) Godot beaucoup plus rapidement que GNU ld ou gold. Cela conduit à des temps d'itération plus rapides.
Clang a tendance à donner des messages d'erreur plus utiles que GCC.
Pour ce faire, installez Clang et le paquet lld du gestionnaire de paquets de votre distribution puis utilisez la commande SCons suivante :
scons platform=linuxbsd use_llvm=yes linker=lld
Une fois la compilation terminée, un nouveau binaire avec un suffixe .llvm sera créé dans le dossier bin/.
Il est toujours recommandé d'utiliser GCC pour les constructions builds de production car ils peuvent être compilés en utilisant l'optimisation du temps de liaison, ce qui rend les binaires résultants plus petits et plus rapides.
Si cette erreur se produit :
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l:libatomic.a: No such file or directory
Il y a deux façon de faire cela :
In your SCons command, add the parameter
use_static_cpp=no.Follow these instructions to configure, build, and install
libatomic_ops. Then, copy/usr/lib/libatomic_ops.ato/usr/lib/libatomic.a, or create a soft link tolibatomic_opsby commandln -s /usr/lib/libatomic_ops.a /usr/lib/libatomic.a. The soft link can ensure the latestlibatomic_opswill be used without the need to copy it everytime when it is updated.
Using mold for faster development¶
For even faster linking compared to LLD, you can use mold. mold can be used with either GCC or Clang.
As of January 2023, mold is not readily available in Linux distribution repositories, so you will have to install its binaries manually.
Download mold binaries from its releases page.
Extract the
.tar.gzfile, then move the extraced folder to a location such as.local/share/mold.Add
$HOME/.local/share/mold/binto your user'sPATHenvironment variable. For example, you can add the following line at the end of your$HOME/.bash_profilefile:
PATH="$HOME/.local/share/mold/bin:$PATH"
Open a new terminal (or run
source "$HOME/.bash_profile"), then use the following SCons command when compiling Godot:scons platform=linuxbsd linker=mold
Using system libraries for faster development¶
Godot bundles the source code of various third-party libraries. You can choose to use system versions of third-party libraries instead. This makes the Godot binary faster to link, as third-party libraries are dynamically linked. Therefore, they don't need to be statically linked every time you build the engine (even on small incremental changes).
However, not all Linux distributions have packages for third-party libraries available (or they may not be up-to-date).
Moving to system libraries can reduce linking times by several seconds on slow CPUs, but it requires manual testing depending on your Linux distribution. Also, you may not be able to use system libraries for everything due to bugs in the system library packages (or in the build system, as this feature is less tested).
To compile Godot with system libraries, install these dependencies on top of the ones listed in the Lignes uniques spécifiques à la distribution:
Fedora |
sudo dnf install embree3-devel enet-devel glslang-devel graphite2-devel harfbuzz-devel libicu-devel \
libsquish-devel libtheora-devel libvorbis-devel libwebp-devel libzstd-devel mbedtls-devel \
miniupnpc-devel
|
After installing all required packages, use the following command to build Godot:
scons platform=linuxbsd builtin_embree=no builtin_enet=no builtin_freetype=no builtin_graphite=no builtin_harfbuzz=no builtin_libogg=no builtin_libpng=no builtin_libtheora=no builtin_libvorbis=no builtin_libwebp=no builtin_mbedtls=no builtin_miniupnpc=no builtin_pcre2=no builtin_zlib=no builtin_zstd=no
You can view a list of all built-in libraries that have system alternatives by
running scons -h, then looking for options starting with builtin_.
Avertissement
When using system libraries, the resulting library is not portable across Linux distributions anymore. Do not use this approach for creating binaries you intend to distribute to others, unless you're creating a package for a Linux distribution.
Utiliser Pyston pour un développement plus rapide¶
Vous pouvez utiliser Pyston pour exécuter SCons. Pyston est une implémentation compatible JIT du langage Python (dans lequel SCons est écrit). Il n'est actuellement compatible qu'avec Linux. Pyston peut accélérer les constructions incrémentales de manière significative, souvent par un facteur compris entre 1,5× et 2×. Pyston peut être combiné avec Clang et LLD pour obtenir des constructions encore plus rapides.
Download the latest portable Pyston release.
Extrayez le fichier portable
.tar.gzvers un emplacement défini, tel que$HOME/.local/opt/pyston/(créez des dossiers si nécessaire).Utilisez
cdpour atteindre le dossier Pyston extrait depuis un terminal, puis exécutez./pyston -m pip install sconspour installer SCons dans Pyston.Pour faciliter l'exécution de SCons via Pyston, créez un lien symbolique de son script wrapper vers un emplacement de votre variable d'environnement
PATH: :ln -s ~/.local/opt/pyston/bin/scons ~/.local/bin/pyston-scons
Au lieu d'exécuter ``scons <build arguments>`, exécutez ``pyston-scons <build arguments>` pour compiler Godot.
Si vous ne pouvez pas exécuter pyston-scons après avoir créé le lien symbolique, assurez-vous que HOME/.local/bin/ fait partie de la variable d'environnement PATH de votre utilisateur.
Note
Alternatively, you can run python -m pip install pyston_lite_autoload
then run SCons as usual. This will automatically load a subset of Pyston's
optimizations in any Python program you run. However, this won't bring as
much of a performance improvement compared to installing "full" Pyston.